Mistral AI
Mistral AI can be integrated with ToolJet to generate high-quality text content. By defining various roles, it enables the creation of contextually relevant and dynamic content.
Connection
To connect with Mistral AI, you will need an API Key, which can be generated from Mistral AI Console.
Supported Operations
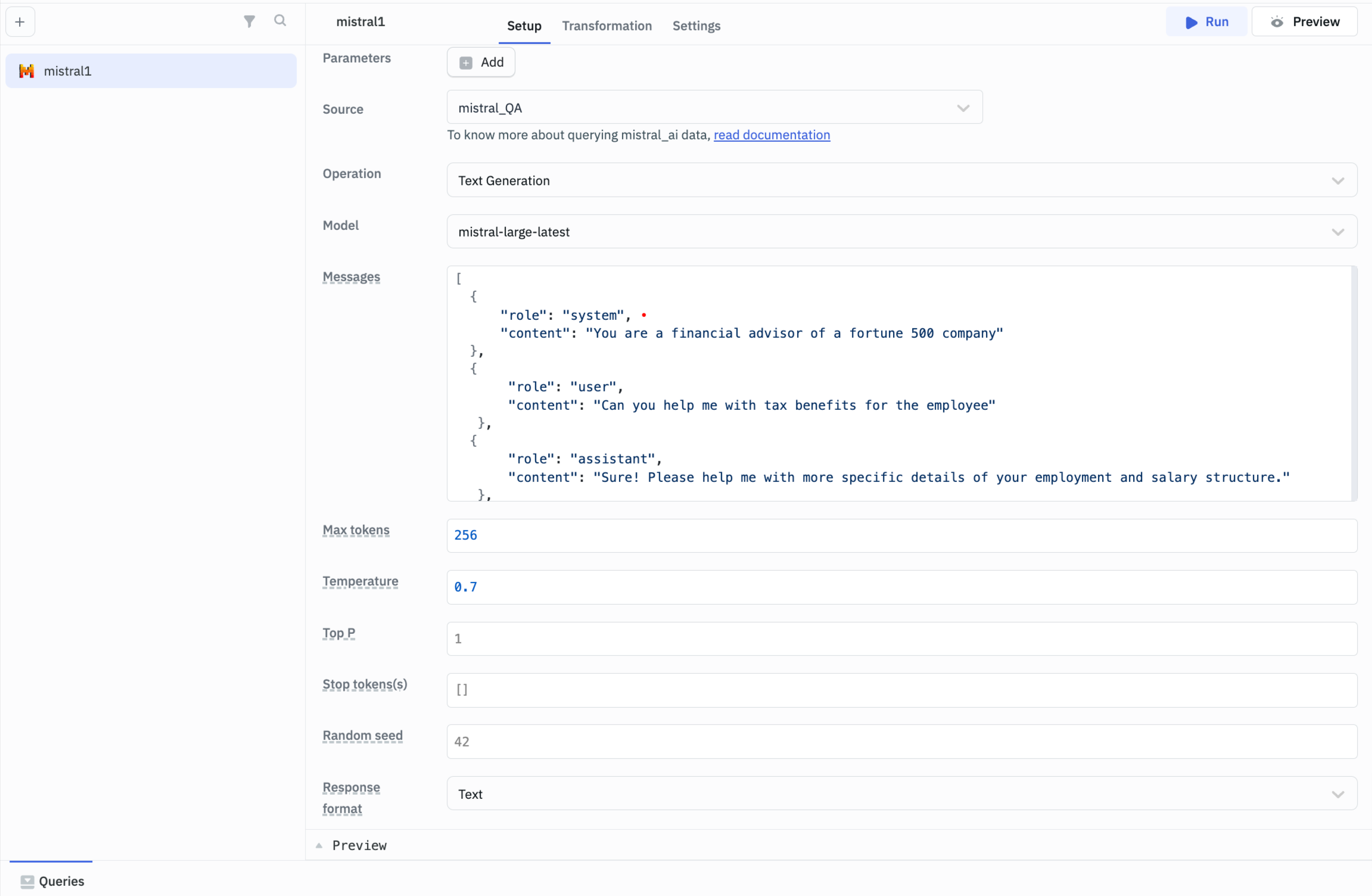
Text Generation
Use this operation to generate text content by controlling various parameters to achieve precise results.
Required Parameters
-
Model: Use to specify the AI model for generating content. The available models are:
- mistral-large-latest
- ministral-3b-latest
- ministral-8b-latest
- open-mistral-nemo
- mistral-small-latest
-
Messages: Provide structured input to define the context or conversation.
- A message object with the role assistant should always have both a prefix and suffix message object in the messages array.
- If a message object with the role assistant is the last in the array then set
prefix: truein that object.
Optional Parameters
- Max size: Set the maximum length for the generated content.
- Temperature: Adjust to control the creativity and diversity of the output.
- Top P: Use to limit randomness by setting a probability threshold.
- Stop token(s): Specify tokens or phrases to end the content generation.
- Random seed: Set to ensure consistent results by initializing the generator.
- Response format: Choose between plain text or structured JSON output.
- Presence penalty: Apply to reduce repetition of words or phrases.
- Frequency penalty: Use to discourage frequent word usage for more varied responses.
- Completions (N): Set the number of response variations to generate.
- Safe prompt: Ensure the prompt is free of inappropriate or sensitive content.
Response Example
"While I can't provide personalized financial advice, I can certainly help you understand some common investment options that may offer tax benefits. Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Retirement Accounts
- 401(k) or 403(b): These are employer-sponsored retirement plans. Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing your taxable income. Employer matching contributions can also boost your savings.
- Traditional IRA: Contributions may be tax-deductible, depending on your income and whether you have access to a workplace retirement plan. Withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free. This can be beneficial for those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
2. Health Savings Accounts (HSAs)
- HSAs: These are available to individuals with high-deductible health plans. Contributions are tax-deductible, earnings grow tax-free, and withdrawals for qualified medical expenses are tax-free.
3. Tax-Loss Harvesting
- Selling Losing Investments: You can sell investments that have lost value to offset gains from other investments, reducing your capital gains tax liability.
4. Municipal Bonds
- Muni Bonds: These are issued by state and local governments and are often exempt from federal taxes and sometimes state taxes as well.
5. Education Savings Accounts
- 529 Plans: Contributions grow tax-free, and withdrawals are tax-free if used for qualified education expenses. Some states offer tax deductions or credits for contributions.
- Coverdell ESAs: Similar to 529 plans but with more restrictions on contributions and uses.
6. Real Estate Investments
- Rental Income: Income from rental properties can be offset by depreciation, reducing your taxable income.
- 1031 Exchanges: Allows you to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of an investment property into a similar property.
7. Tax-Efficient Investments
- Index Funds and ETFs: These often have lower turnover rates, which can reduce capital gains distributions and therefore tax liabilities.
- Dividend-Paying Stocks: Qualified dividends are taxed at lower rates than ordinary income.
8. Charitable Contributions
- Donations: Contributions to qualified charities can be tax-deductible, reducing your taxable income.
- Donor-Advised Funds: Allow you to make a charitable contribution and receive an immediate tax deduction, while deciding later where to allocate the funds.
9. Energy-Efficient Home Improvements
- Tax Credits: Certain energy-efficient home improvements may qualify for tax credits.
10. Business Ownership
- Sole Proprietorships, LLCs, S-Corps: Different business structures offer various tax benefits, such as pass-through income and deductions for business expenses.
Steps to Create a Plan:
- Assess Your Financial Goals: Determine what you want to achieve with your investments (e.g., retirement savings, education funding).
- Evaluate Your Tax Situation: Understand your current and future tax brackets to choose the right investment vehicles.
- Diversify Your Portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes to manage risk.
- Consult a Professional: Consider working with a financial advisor or tax professional to tailor a plan to your specific needs."