Multi-Environment
Environments in ToolJet help manage different stages of application development, ensuring smooth transitions between development, testing, and production. This guide covers what environments are, their purpose, and how they function in ToolJet.
Environments make it easier to develop and deploy applications without disrupting production. They keep changes isolated, so testing and debugging can happen without affecting live users. Teams can collaborate more efficiently, as different environments allow them to work independently.
What are Environments?
An environment in ToolJet represents a separate configuration space where applications, data sources, and constants can be defined and managed.
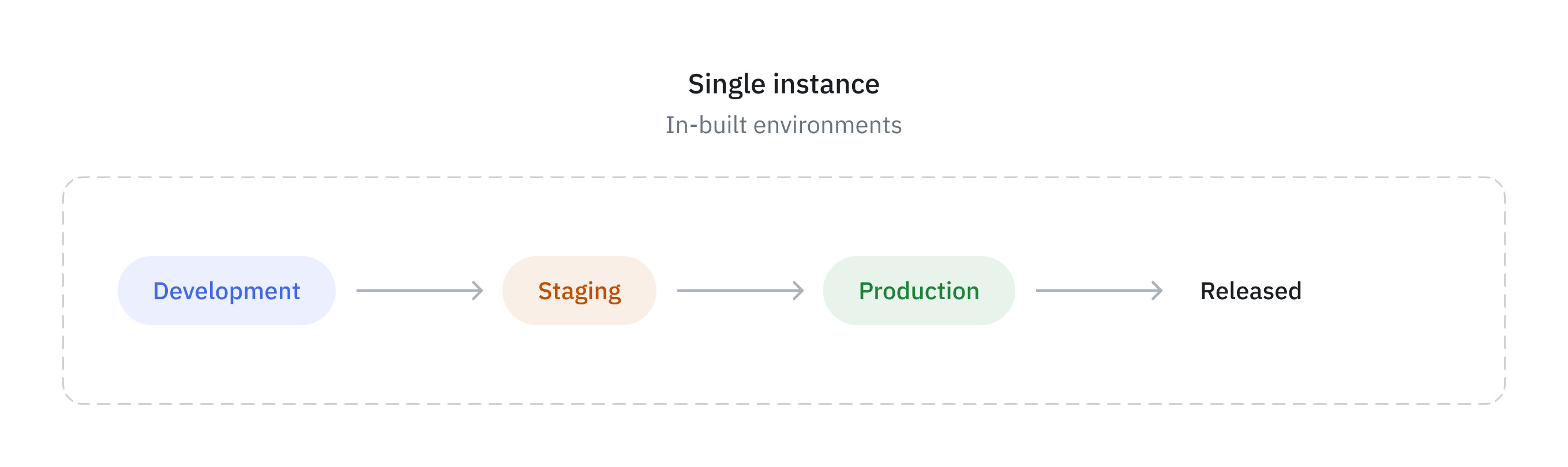
By default, ToolJet provides three environments:
-
Development: The Development environment is where application development and initial testing take place. It is a dedicated space for ToolJet developers to build, configure, and experiment with application features. Changes in this environment do not affect live users, allowing for frequent updates and debugging.
-
Staging: The Staging environment acts as a pre-production space where applications undergo thorough testing before deployment. It closely resembles the Production environment and helps ensure that all features, performance, and security aspects function as expected. Teams such as QA and product managers use this environment to validate and approve changes before releasing them to end-users.
-
Production: The Production environment is the final, live version of the application where end users interact with it. This environment is stable and optimized for performance after thorough testing in the Development and Staging environments.
Multi-Environment Support in ToolJet
ToolJet provides environment management across different components:
Applications
Each application has development, staging, and production environments. Developers build the application in the development environment and then move it to staging for testing. Your testing team can review the application in staging, and once it's thoroughly tested, you can promote it to production and release it to your end users.
Data Sources
Data sources can be configured separately for each environment, allowing applications to connect to different databases or APIs depending on the environment. This ensures secure and structured access to relevant data during each stage of development.
Constants
Constants such as API keys, credentials, or other configuration variables can be defined uniquely for each environment. This helps maintain security and prevents misconfigurations across different deployment stages.
Application Life cycle
The application lifecycle in ToolJet involves managing applications across different environments development, staging, and production. You can build the application in development environment and promote it to staging for testing. After testing you can promote it to production and release the app for your end-users.
You can configure data sources and constants for each environment, and ToolJet will automatically use the appropriate ones based on the target environment.
-
Development – Developers build and test the application in the ToolJet app builder.
-
Staging – The testing or product team validates requirements and tests the application using staging data. Apps and queries cannot be edited in this environment.
-
Production – After thorough testing in staging, the application is promoted to production. This can serve as a pre-release environment where you test with production data and constants before releasing the application to end users. Refer to Release documentation to learn more.
Impacted behavior with environment permission
Each environment has a different impact on your application. Please refer the following table for details.
| Action | Development | Staging | Production |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edit versions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Rename versions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Delete versions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Create new versions | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
| Promote | ✅ | ✅ | - |
Checkout the Environment-Example guide to learn about multi-environment in ToolJet with a practical example.
Promote Application Permission
Admin can configure the Promote Application permission from the Permissions page. This disables the Promote button for users who do not have the required permission, allowing only authorized roles, such as team leads, to promote the application from one environment to another.