Deploying ToolJet on Openshift
To use ToolJet AI features in your deployment, make sure to whitelist https://api-gateway.tooljet.ai and https://python-server.tooljet.ai in your network settings.
You should setup a PostgreSQL database manually to be used by ToolJet. You can find the system requirements here.
ToolJet runs with built-in Redis for multiplayer editing and background jobs. When running separate worker containers or multi-pod setup, an external Redis instance is required for job queue coordination.
Follow the steps below to deploy ToolJet on Openshift.
-
Setup a PostgreSQL database ToolJet uses a postgres database as the persistent storage for storing data related to users and apps.
TOOLJET_HOST=<Endpoint url>
LOCKBOX_MASTER_KEY=<generate using openssl rand -hex 32>
SECRET_KEY_BASE=<generate using openssl rand -hex 64>
PG_USER=<username>
PG_HOST=<postgresql-database-host>
PG_PASS=<password>
PG_DB=tooljet_production # Must be a unique database name (do not reuse across deployments)Also, for setting up additional environment variables in the .env file, please check our documentation on environment variables here.
-
Once you have logged into the Openshift developer dashboard click on
+Addtab. Select import YAML from the local machine.noteWhen entering one or more files and use --- to separate each definition
Copy paste deployment.yaml to the online editor
curl -LO https://tooljet-deployments.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/openshift/deployment.yamlCopy paste the service.yaml to the online editor
curl -LO https://tooljet-deployments.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/openshift/service.yaml
Once you have added the files click on create.
infoIf there are self signed HTTPS endpoints that Tooljet needs to connect to, please make sure that
NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTSenvironment variable is set to the absolute path containing the certificates. You can make use of kubernetes secrets to mount the certificate file onto the containers. -
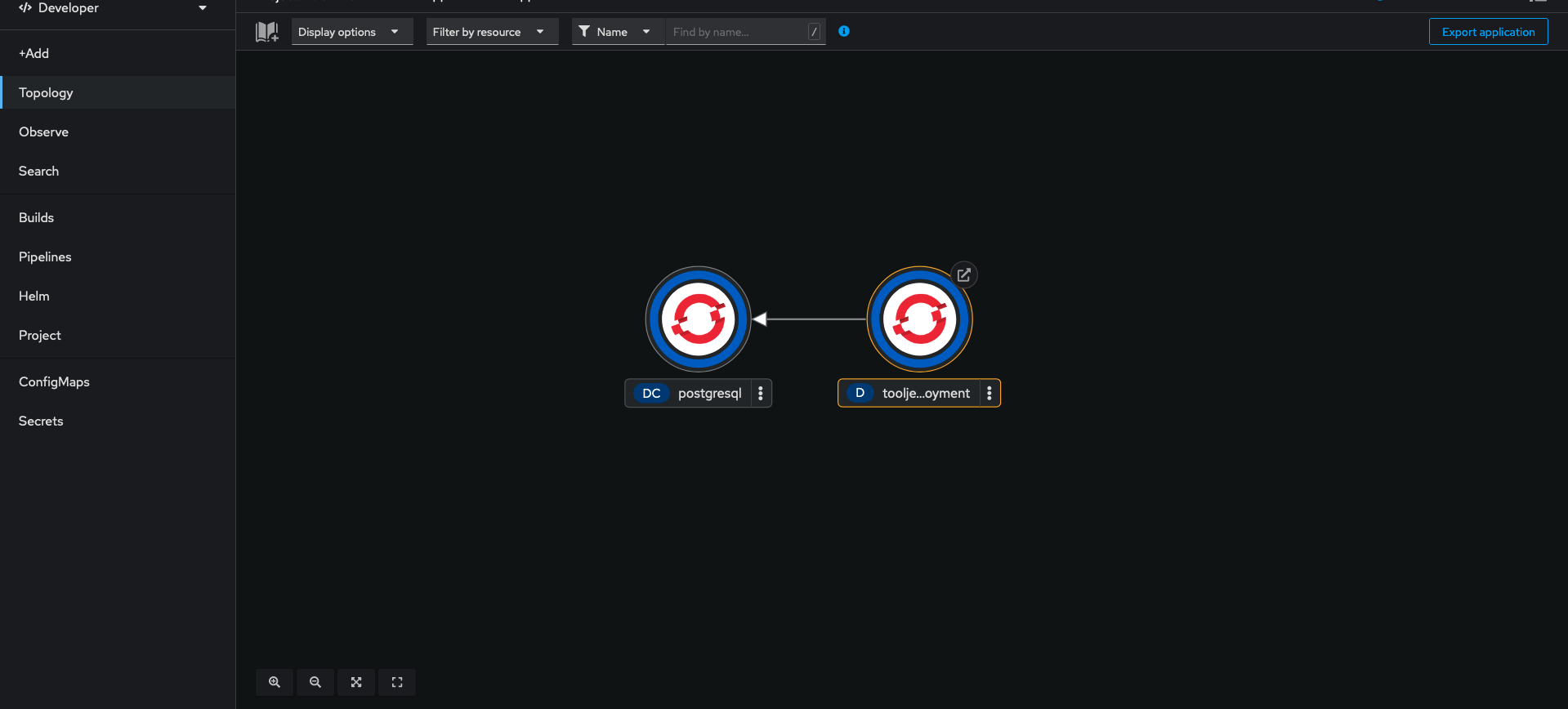
Navigate to topology tab and use the visual connector to establish the connect between tooljet-deployment and postgresql as shown in the screenshot below.
ToolJet Database
Use the ToolJet-hosted database to build apps faster, and manage your data with ease. You can learn more about this feature here.
Deploying ToolJet Database is mandatory from ToolJet 3.0 or else the migration might break. Checkout the following docs to know more about new major version, including breaking changes that require you to adjust your applications accordingly:
Setting Up ToolJet Database
To set up ToolJet Database, the following environment variables are mandatory and must be configured:
TOOLJET_DB=tooljet_db # Must be a unique database name (separate from PG_DB and not shared)
TOOLJET_DB_HOST=<postgresql-database-host>
TOOLJET_DB_USER=<username>
TOOLJET_DB_PASS=<password>
Ensure that TOOLJET_DB is not the same as PG_DB. Both databases must be uniquely named and not shared.
Additionally, for PostgREST, the following mandatory environment variables must be set:
If you have openssl installed, you can run the
command openssl rand -hex 32 to generate the value for PGRST_JWT_SECRET.
If this parameter is not specified, PostgREST will refuse authentication requests.
PGRST_HOST=localhost:3001
PGRST_LOG_LEVEL=info
PGRST_DB_PRE_CONFIG=postgrest.pre_config
PGRST_SERVER_PORT=3001
PGRST_DB_URI=
PGRST_JWT_SECRET=
The PGRST_DB_URI variable is required for PostgREST, which exposes the database as a REST API. This must be explicitly set for proper functionality.
Format:
PGRST_DB_URI=postgres://TOOLJET_DB_USER:TOOLJET_DB_PASS@TOOLJET_DB_HOST:5432/TOOLJET_DB
Ensure these configurations are correctly set up before proceeding with the ToolJet deployment. Make sure these environment variables are set in the same environment as the ToolJet deployment.
Workflows
ToolJet Workflows allows users to design and execute complex, data-centric automations using a visual, node-based interface. This feature enhances ToolJet's functionality beyond building secure internal tools, enabling developers to automate complex business processes.
For users migrating from Temporal-based workflows, please refer to the Workflow Migration Guide.
Enabling Workflow Scheduling
To activate workflow scheduling, set the following environment variables in your ToolJet deployment:
# Worker Mode (required)
# Set to 'true' to enable job processing
# Set to 'false' or unset for HTTP-only mode (scaled deployments)
WORKER=true
# Workflow Processor Concurrency (optional)
# Number of workflow jobs processed concurrently per worker
# Default: 5
TOOLJET_WORKFLOW_CONCURRENCY=5
Environment Variable Details:
- WORKER (required): Enables job processing. Set to
trueto activate workflow scheduling - TOOLJET_WORKFLOW_CONCURRENCY (optional): Controls the number of workflow jobs processed concurrently per worker instance. Default is 5 if not specified
External Redis Requirement: When running separate worker containers or multiple instances, an external stateful Redis instance is required for job queue coordination. The built-in Redis only works when the server and worker are in the same container instance (single instance deployment).
Deploying Redis for Workflows
Deploy a stateful Redis instance using the following example configuration:
kubectl apply -f https://tooljet-deployments.s3.us-west-1.amazonaws.com/kubernetes/redis-stateful.yaml
Built-in Redis vs External Redis
ToolJet images include a built-in Redis instance for development. When deploying workflows in production, you must update your deployment configuration to use the external stateful Redis:
Change REDIS_HOST from localhost to redis-service in your deployment YAML:
- name: REDIS_HOST
value: redis-service # Changed from localhost
- name: REDIS_PORT
value: "6379"
This example deployment creates:
- A StatefulSet with persistent storage for Redis
- A headless Service for stable network identity
- ConfigMap with production-ready Redis configuration
- A Secret for optional password authentication
This is an example configuration that you can customize to your needs. However, AOF (Append Only File) persistence and maxmemory-policy noeviction are critical settings that must be maintained for BullMQ job queue reliability.
After deploying Redis, configure ToolJet to connect to it using these environment variables in your deployment:
REDIS_HOST=redis-service.default.svc.cluster.local
REDIS_PORT=6379
REDIS_PASSWORD=your-secure-redis-password-here # Match the password in redis-secret
Optional Redis Configuration:
REDIS_USERNAME=- Redis username (ACL)REDIS_DB=0- Redis database number (default: 0)REDIS_TLS=false- Enable TLS/SSL (set to 'true')
Note: Update the redis-secret in the Redis deployment YAML with a secure password before deploying to production.
Note: Ensure that these environment variables are added to your OpenShift deployment configuration (e.g., in your deployment.yaml file).
Upgrading to the Latest LTS Version
New LTS versions are released every 3-5 months with an end-of-life of atleast 18 months. To check the latest LTS version, visit the ToolJet Docker Hub page. The LTS tags follow a naming convention with the prefix LTS- followed by the version number, for example tooljet/tooljet:ee-lts-latest.
If this is a new installation of the application, you may start directly with the latest version. This guide is not required for new installations.
Prerequisites for Upgrading to the Latest LTS Version:
-
It is crucial to perform a comprehensive backup of your database before starting the upgrade process to prevent data loss.
-
Users on versions earlier than v2.23.0-ee2.10.2 must first upgrade to this version before proceeding to the LTS version.
If you have any questions feel free to join our Slack Community or send us an email at [email protected].