Deploying ToolJet on Azure Container Apps
To use ToolJet AI features in your deployment, make sure to whitelist https://api-gateway.tooljet.ai and https://python-server.tooljet.ai in your network settings.
Please note that you need to set up a PostgreSQL database manually to be used by ToolJet.
ToolJet runs with built-in Redis for multiplayer editing and background jobs. When running separate worker containers or multi-pod setup, an external Redis instance is required for job queue coordination.
Deploying ToolJet Application
-
Open the Azure dashboard and navigate to Container Apps, then click on Create container app.
-
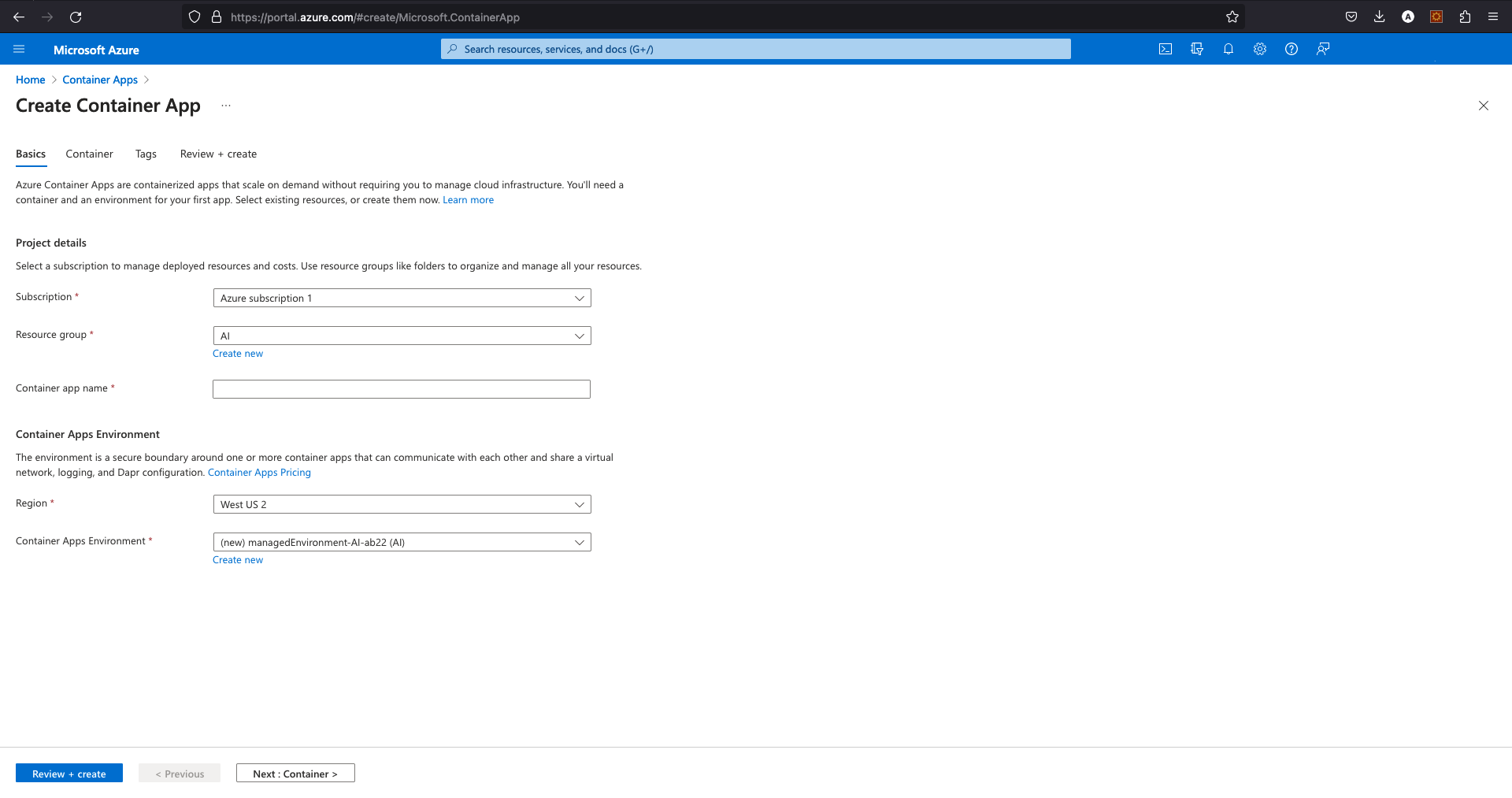
Select the appropriate subscription and provide basic details such as the container name and then click on the Create new environment button below "Container Apps environment" to configure the networking setup.
-
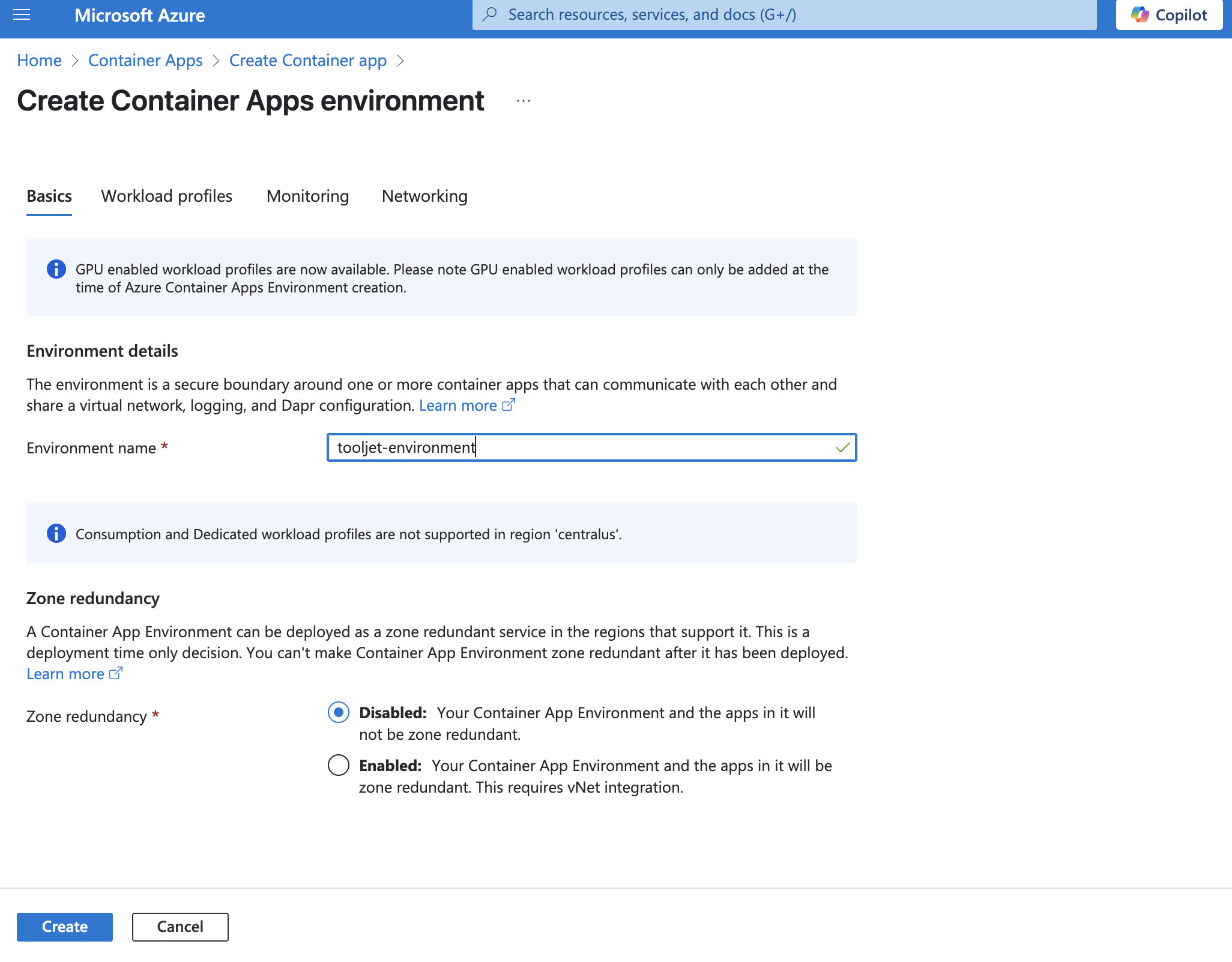
Configure the basic settings as shown in the screenshot below.
-
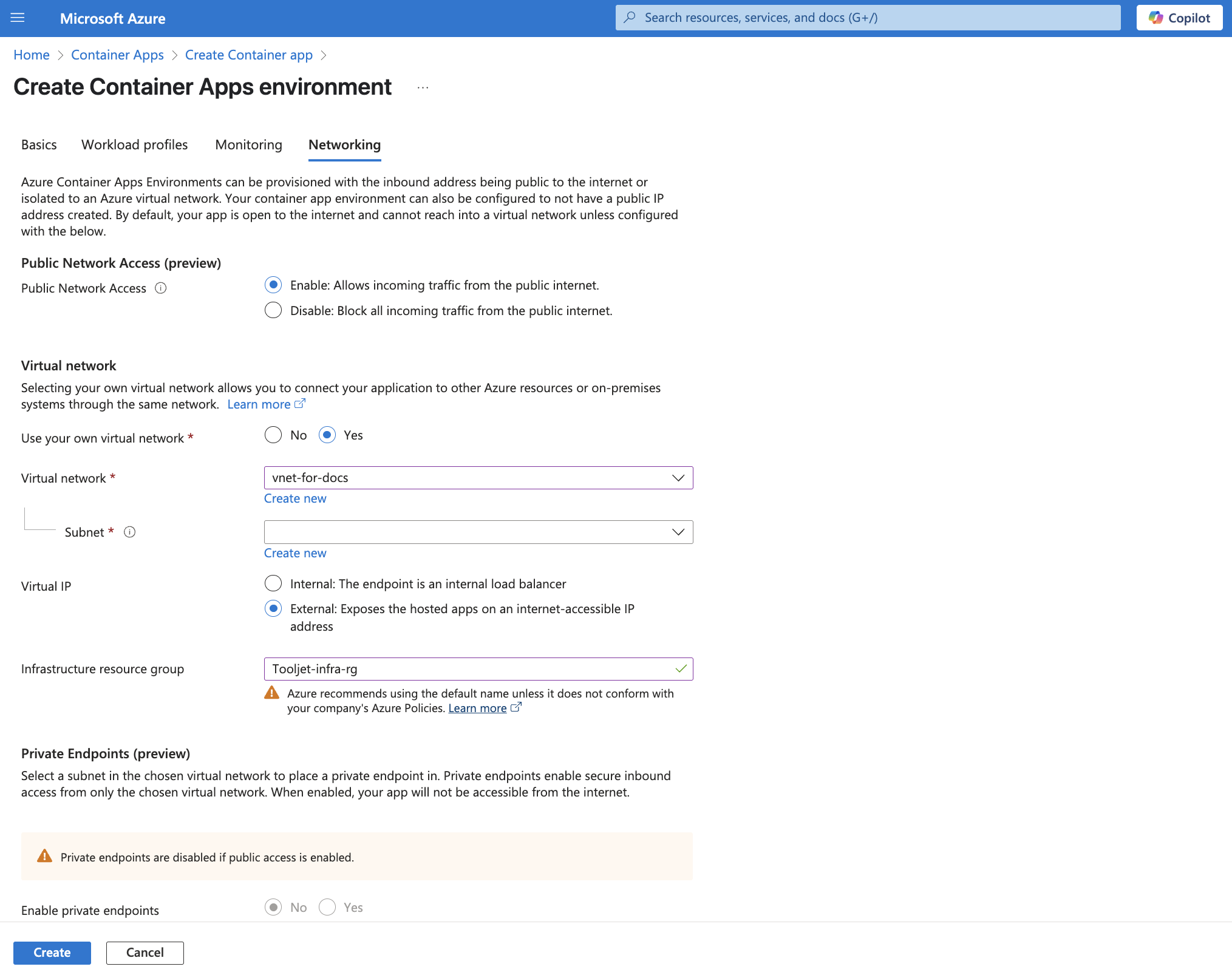
Move to the "Networking" tab for the detailed configuration as shown in the screenshot. You can retain the default settings for Workload Profiles and Monitoring configurations.
tipThe Container app, the PostgreSQL server, and the Redis server all should be in the same virtual network (VNet).
-
Click on the Create button at the bottom of the page.
-
Then you will be redirected to the Create Container App tab, uncheck the Use quickstart image option to select the image source manually. Make sure to provide the image tag, and then enter
server/ee-entrypoint.sh, npm, run, start:prodin the "Arguments override" field.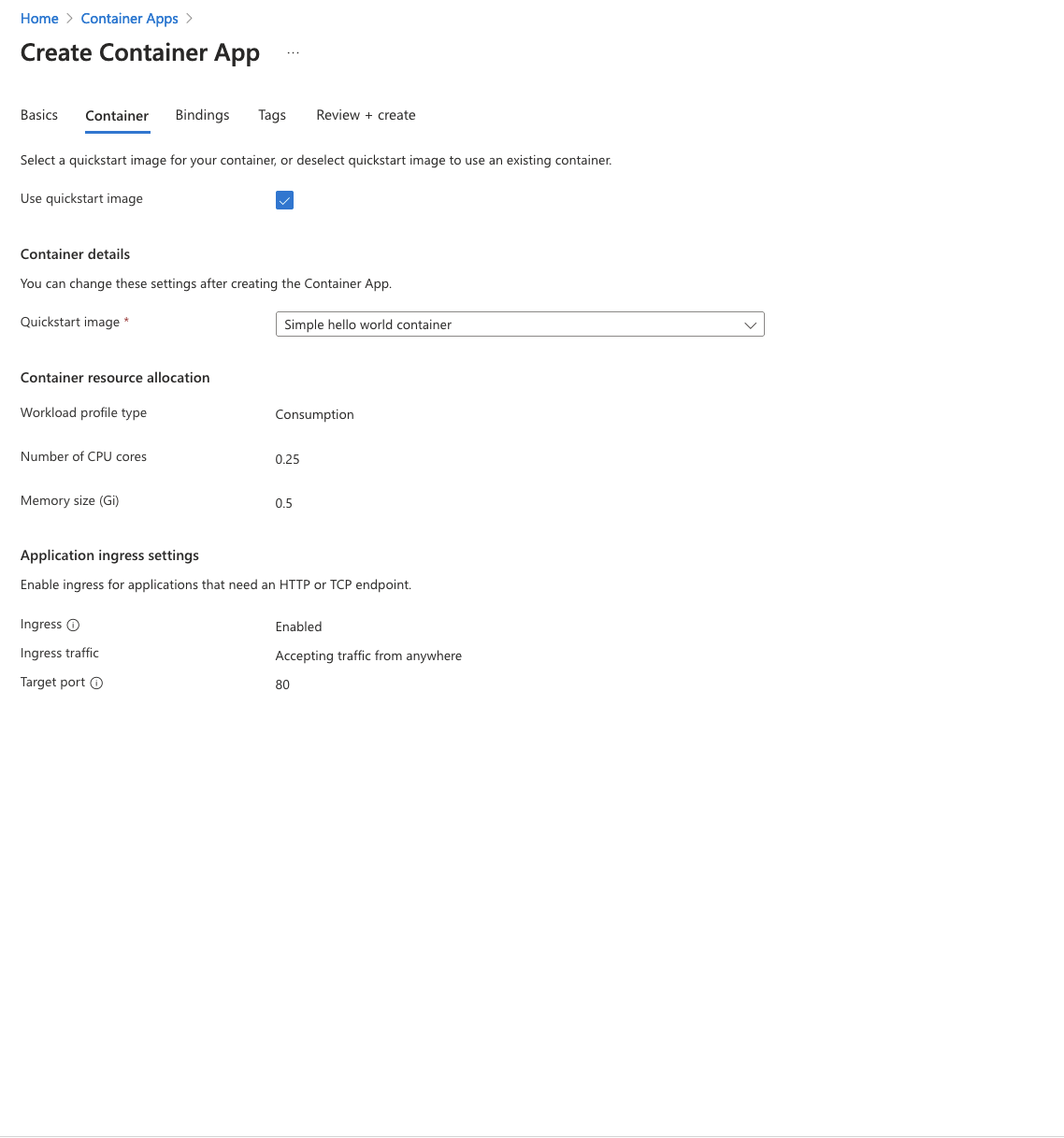
-
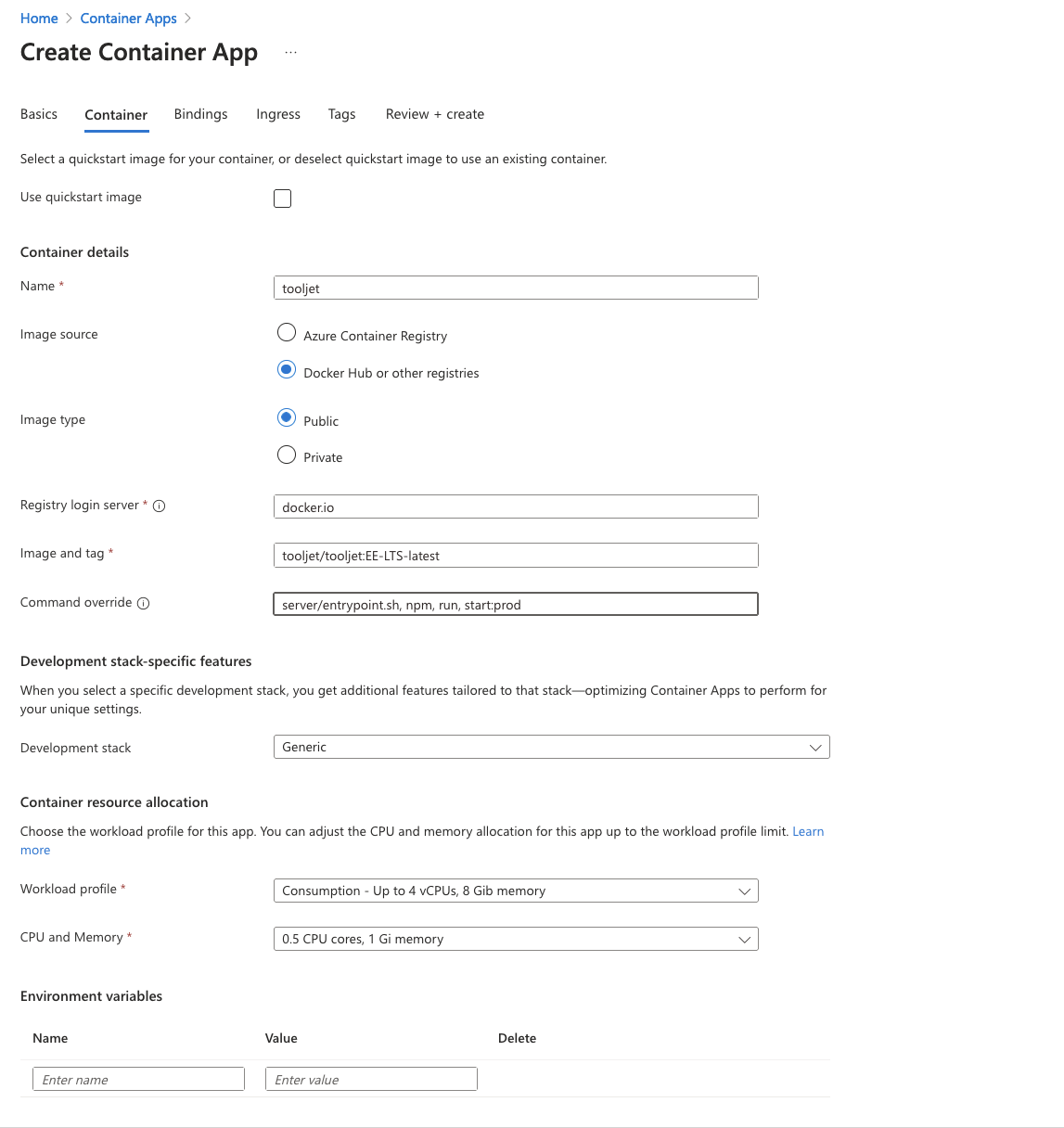
Under "Environmental variables", please add the below ToolJet application variables:
TOOLJET_HOST=<Endpoint url>
LOCKBOX_MASTER_KEY=<generate using 'openssl rand -hex 32'>
SECRET_KEY_BASE=<generate using 'openssl rand -hex 64'>
PG_USER=<username>
PG_HOST=<postgresql-instance-ip>
PG_PASS=<password>
PG_DB=tooljet_production # Must be a unique database name (do not reuse across deployments)Update the
TOOLJET_HOSTenvironment variable to reflect the default host assigned by Azure Container Apps, if you're not using a custom domain.If using Azure Database for Postgresql-Flexible server, also add:
PGSSLMODE = requireTo set up ToolJet Database, the following environment variables are mandatory and must be configured:
TOOLJET_DB=tooljet_db # Must be a unique database name (separate from PG_DB and not shared)
TOOLJET_DB_HOST=<postgresql-database-host>
TOOLJET_DB_USER=<username>
TOOLJET_DB_PASS=<password>noteEnsure that
TOOLJET_DBis not the same asPG_DB. Both databases must be uniquely named and not shared.Additionally, for PostgREST, the following mandatory environment variables must be set in Tooljet container:
tipIf you have openssl installed, you can run the command
openssl rand -hex 32to generate the value forPGRST_JWT_SECRET.If this parameter is not specified, PostgREST will refuse authentication requests.
PGRST_HOST=127.0.0.1:3002
PGRST_JWT_SECRET=Ensure these configurations are correctly set up before proceeding with the ToolJet deployment. Make sure these environment variables are set in the same environment as the ToolJet container.
Note: These environment variables are in general and might change in the future. You can also refer env variable here.
-
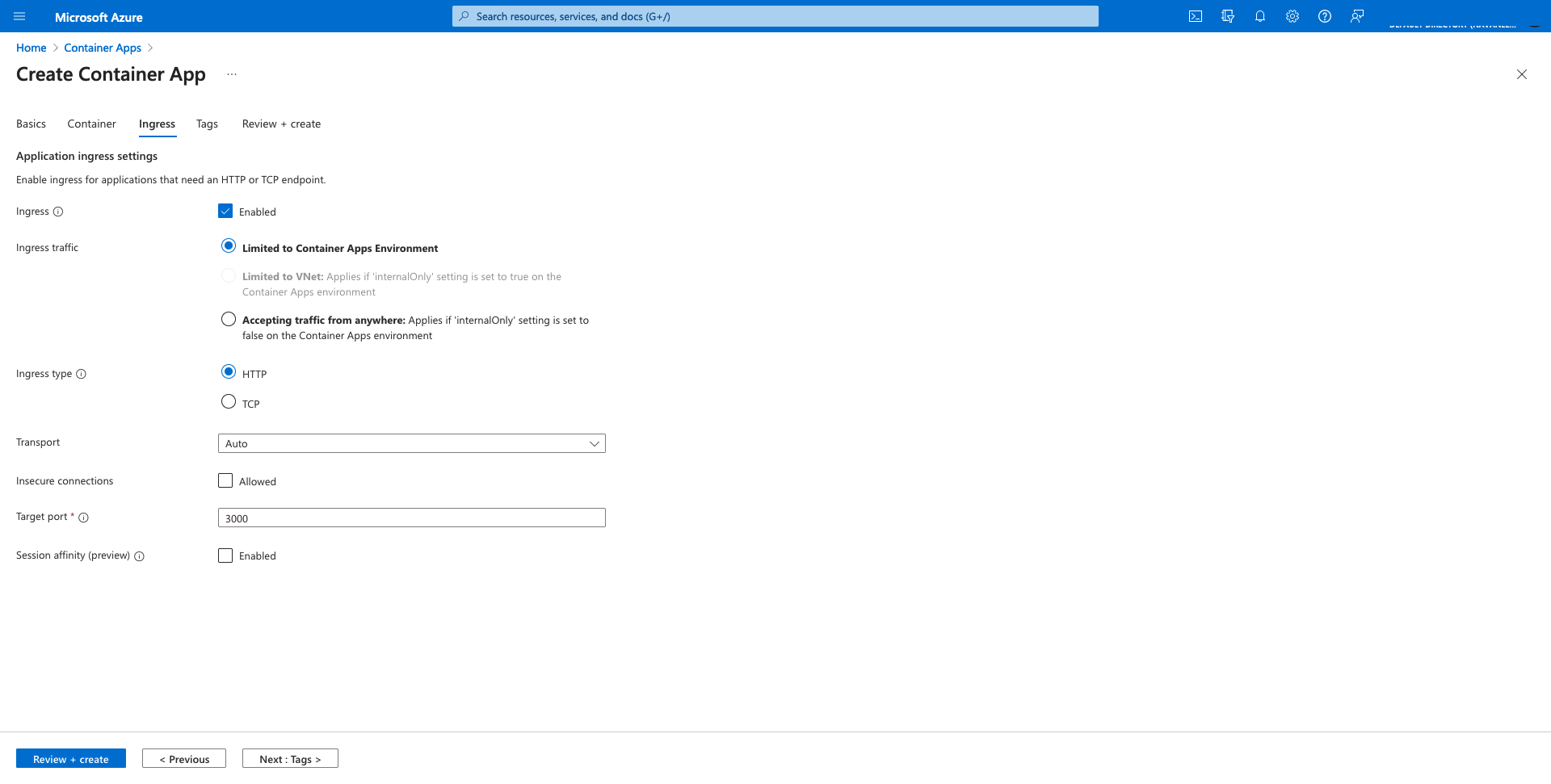
In the Ingress tab, configure Ingress and Authentication settings as shown below. You can customize the security configurations as per your requirements. Make sure the port is set to 3000.
-
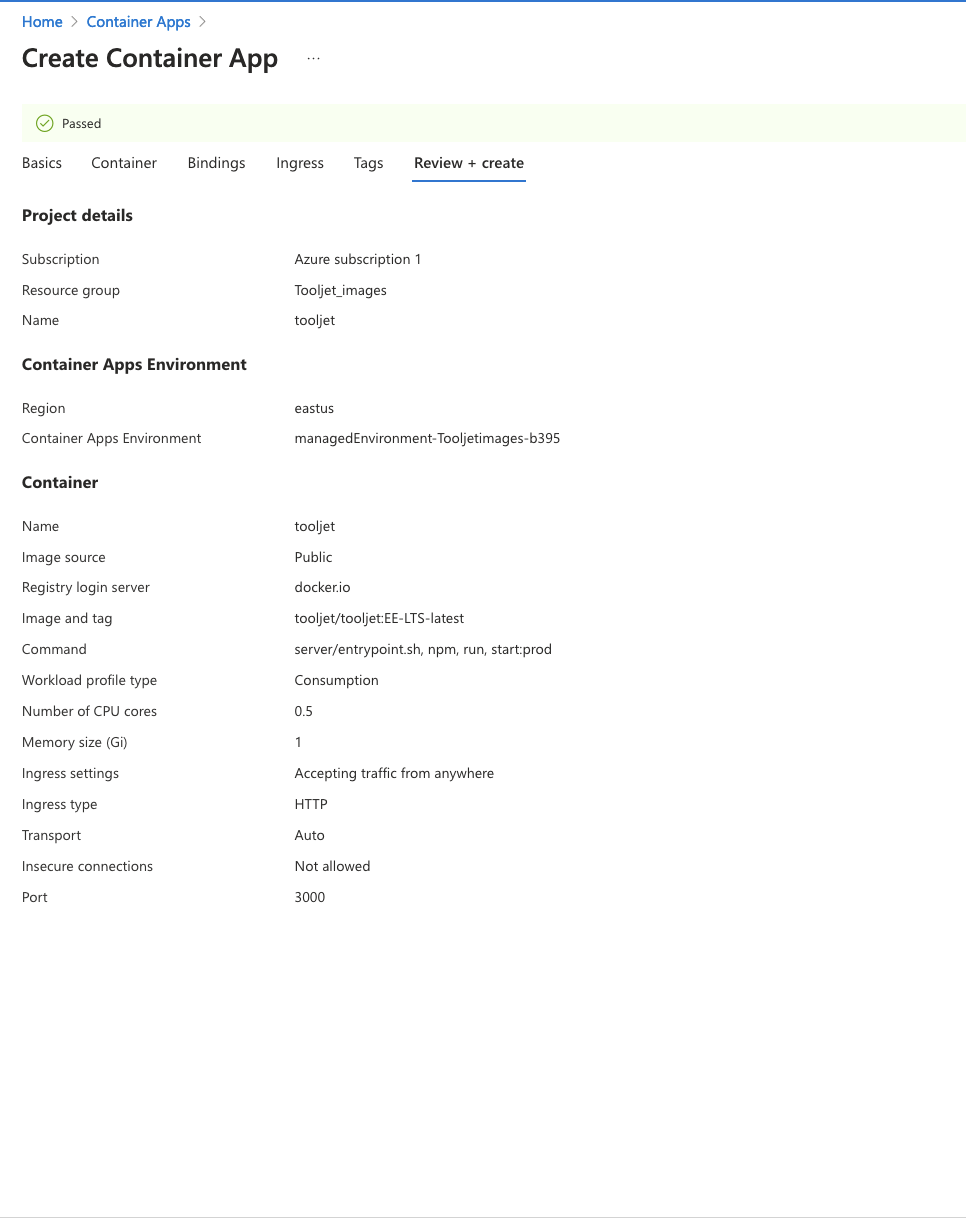
Move to Review + create tab and wait for the template to be verified and passed, as shown in the screenshot below.
-
Once the container is deployed, you can verify its status under revision management.
Deploying Postgrest container
-
To enable PostgREST functionality alongside ToolJet, you must
create new containerwithin your deployment configuration. This container will run PostgREST as a sidecar service, which is essential for enabling RESTful access to your PostgreSQL database.
Without this setup, you may encounter connection errors
ERR ::1 ECONNREFUSEDAfter selecting
Create new container, configure the container to run PostgREST using the appropriate image and environment variables.Use the official PostgREST image:
postgrest/postgrest:12.2.0
Under
Environment variablessection ensure the following variables are set within the PostgREST container:PGRST_LOG_LEVEL=info
PGRST_DB_PRE_CONFIG=postgrest.pre_config
PGRST_SERVER_PORT=3002
PGRST_DB_URI=
PGRST_JWT_SECRET=The
PGRST_DB_URIvariable is required for PostgREST, which exposes the database as a REST API. This must be explicitly set for proper functionality. Also ensurePGRST_JWT_SECRETvalue is same in both the containers.Format:
PGRST_DB_URI=postgres://TOOLJET_DB_USER:TOOLJET_DB_PASS@TOOLJET_DB_HOST:5432/TOOLJET_DBOnce the new container is created and deployed, ToolJet can interact with PostgREST, and you can access the application using the URL shown in the Overview tab of Azure Container Apps.
ToolJet Database
Use the ToolJet-hosted database to build apps faster, and manage your data with ease. You can learn more about this feature here.
Deploying ToolJet Database is mandatory from ToolJet 3.0 or else the migration might break. Checkout the following docs to know more about new major version, including breaking changes that require you to adjust your applications accordingly:
Workflows
ToolJet Workflows allows users to design and execute complex, data-centric automations using a visual, node-based interface. This feature enhances ToolJet's functionality beyond building secure internal tools, enabling developers to automate complex business processes.
For users migrating from Temporal-based workflows, please refer to the Workflow Migration Guide.
Enabling Workflow Scheduling
To activate workflow scheduling, set the following environment variables:
# Worker Mode (required)
# Set to 'true' to enable job processing
# Set to 'false' or unset for HTTP-only mode (scaled deployments)
WORKER=true
# Workflow Processor Concurrency (optional)
# Number of workflow jobs processed concurrently per worker
# Default: 5
TOOLJET_WORKFLOW_CONCURRENCY=5
Environment Variable Details:
- WORKER (required): Enables job processing. Set to
trueto activate workflow scheduling - TOOLJET_WORKFLOW_CONCURRENCY (optional): Controls the number of workflow jobs processed concurrently per worker instance. Default is 5 if not specified
External Redis Requirement: When running separate worker containers or multiple instances, an external stateful Redis instance is required for job queue coordination. The built-in Redis only works when the server and worker are in the same container instance (single instance deployment). Configure the Redis connection using the following environment variables:
REDIS_HOST=localhost- Default: localhostREDIS_PORT=6379- Default: 6379REDIS_USERNAME=- Optional: Redis username (ACL)REDIS_PASSWORD=- Optional: Redis passwordREDIS_DB=0- Optional: Redis database number (default: 0)REDIS_TLS=false- Optional: Enable TLS/SSL (set to 'true')
Upgrading to the Latest LTS Version
New LTS versions are released every 3-5 months with an end-of-life of atleast 18 months. To check the latest LTS version, visit the ToolJet Docker Hub page. The LTS tags follow a naming convention with the prefix LTS- followed by the version number, for example tooljet/tooljet:ee-lts-latest.
If this is a new installation of the application, you may start directly with the latest version. This guide is not required for new installations.
Prerequisites for Upgrading to the Latest LTS Version:
- It is crucial to perform a comprehensive backup of your database before starting the upgrade process to prevent data loss.
- Users on versions earlier than v2.23.0-ee2.10.2 must first upgrade to this version before proceeding to the LTS version.
If you have any questions feel free to join our Slack Community or send us an email at [email protected].