Workspace Constants
ToolJet allows you to set workspace constants to store pre-defined values that can be used across your application to maintain consistency, facilitate easy updates, and securely store sensitive information. Workspace constants are specific to the workspace where they are created and cannot be accessed in other workspaces. To enhance security, all constants and secrets are encrypted before being stored in the database, providing an additional layer of protection for sensitive data.
There are two types of constants:
- Global Constants: These are predefined values that can be used across your applications within a workspace. They allow you to store frequently used values, such as API URLs, configuration settings, etc. and access them within the workspace. Global Constants are resolved on the client side.
- Secret Constants: These are a specific type of workspace constants designed for securely storing sensitive information like API keys and database credentials. Secrets are masked and stored in encrypted format to prevent exposure to unauthorized users. Secret Constants are resolved on the server side, preventing exposure to the client.
Note: Secret Constants cannot be used in RunJS or RunPy queries.
Characteristics and Usage
| Characteristic | Global Constants | Secrets |
|---|---|---|
| Components | ✅ | ❌ |
| Data Queries | ✅ | ✅ |
| Data Sources | ✅ | ✅ |
| Workflows | ✅ | Coming Soon |
| Encrypted in DB | ✅ | ✅ |
| Masked in Frontend | ❌ | ✅ |
| Resolved on Client Side | ✅ | ❌ |
| Resolved on Server Side | ❌ | ✅ |
| Naming Convention | {{constants.constant_name}} | {{secrets.secret_name}} |
Note:
- Secret Constants cannot be used in RunJS or RunPy queries.
- Secret Constants can only be used as a singular key and can't be used in a composite key manner.
Environment Specific Configurations
ToolJet allows users to define environment-specific configurations by assigning different values to constants and secrets across various environments. This approach is essential for managing sensitive information, such as API keys, database credentials, and external service endpoints, which may differ between development, staging, and production environments.
For example, you can configure unique API keys for each environment to ensure seamless integration and security.
Creating Workspace Constants
Workspace constants/variables permissions is needed to Create, Update or Delete workspace constants, refer to Access Control guide for more information. After having the required permission, follow these steps to create a workspace constant:
-
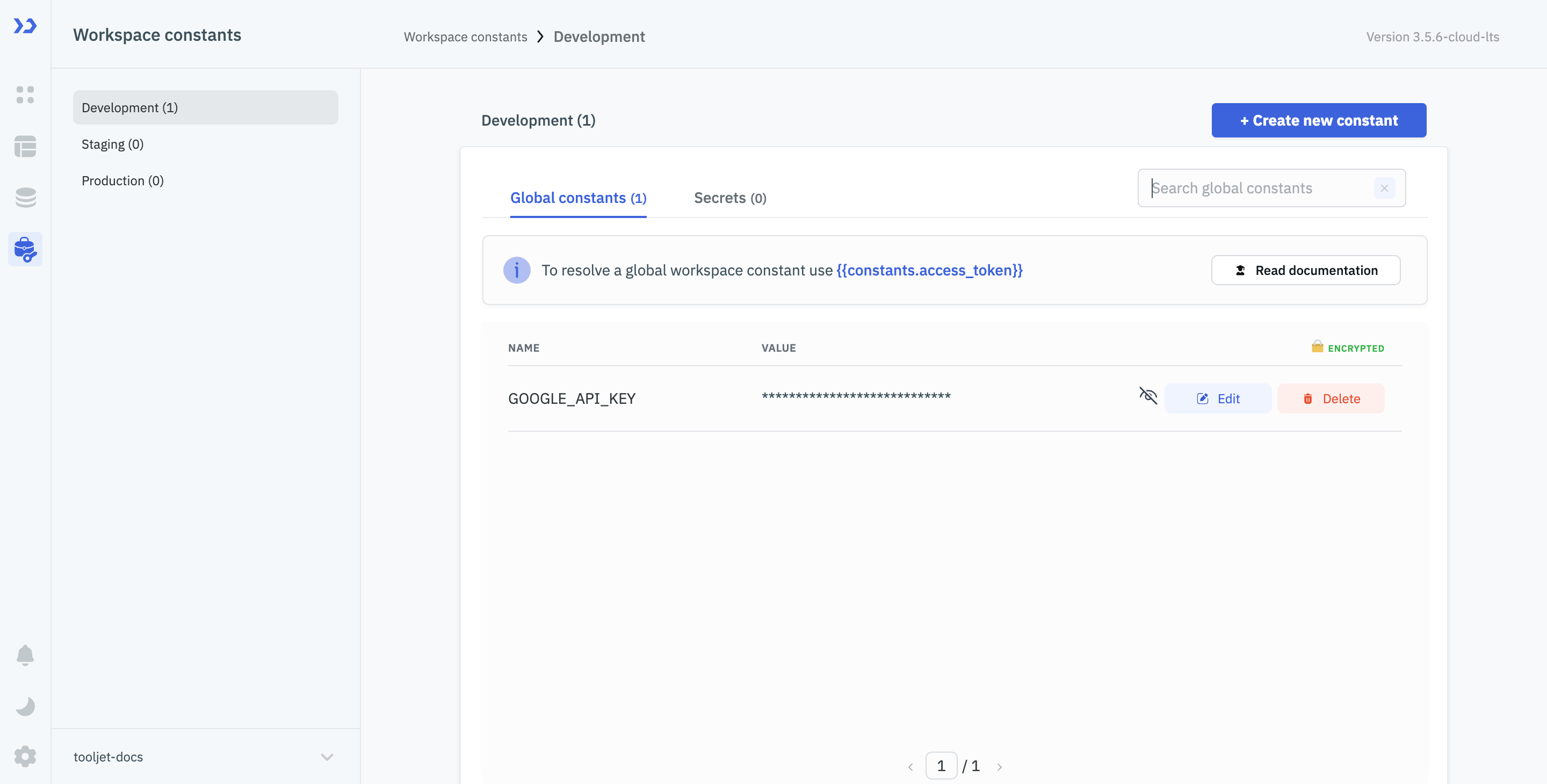
Navigate to the Workspace Constants tab from the left sidebar in ToolJet dashboard.
(Example URL -https://app.corp.com/nexus/workspace-constants)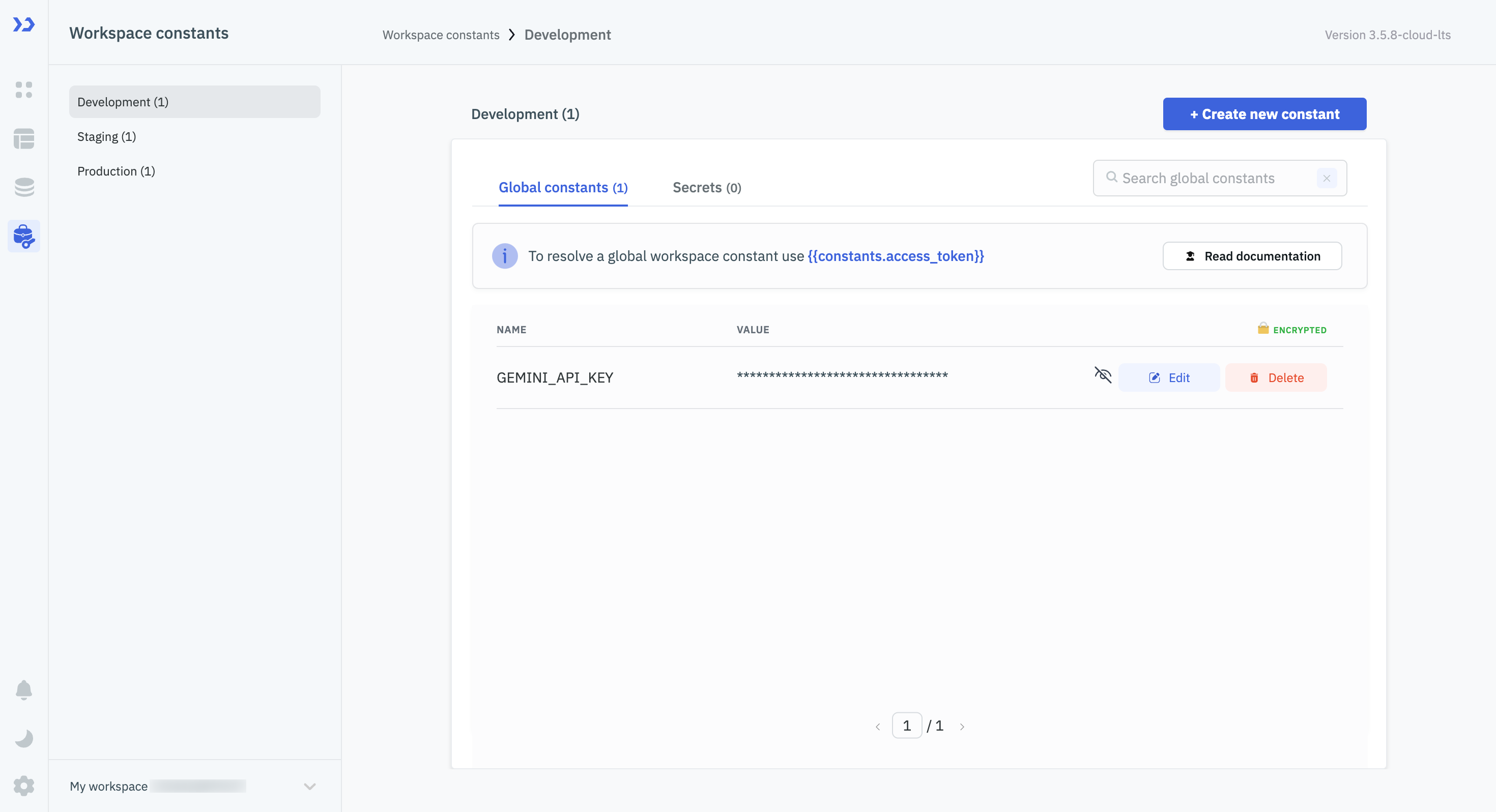
-
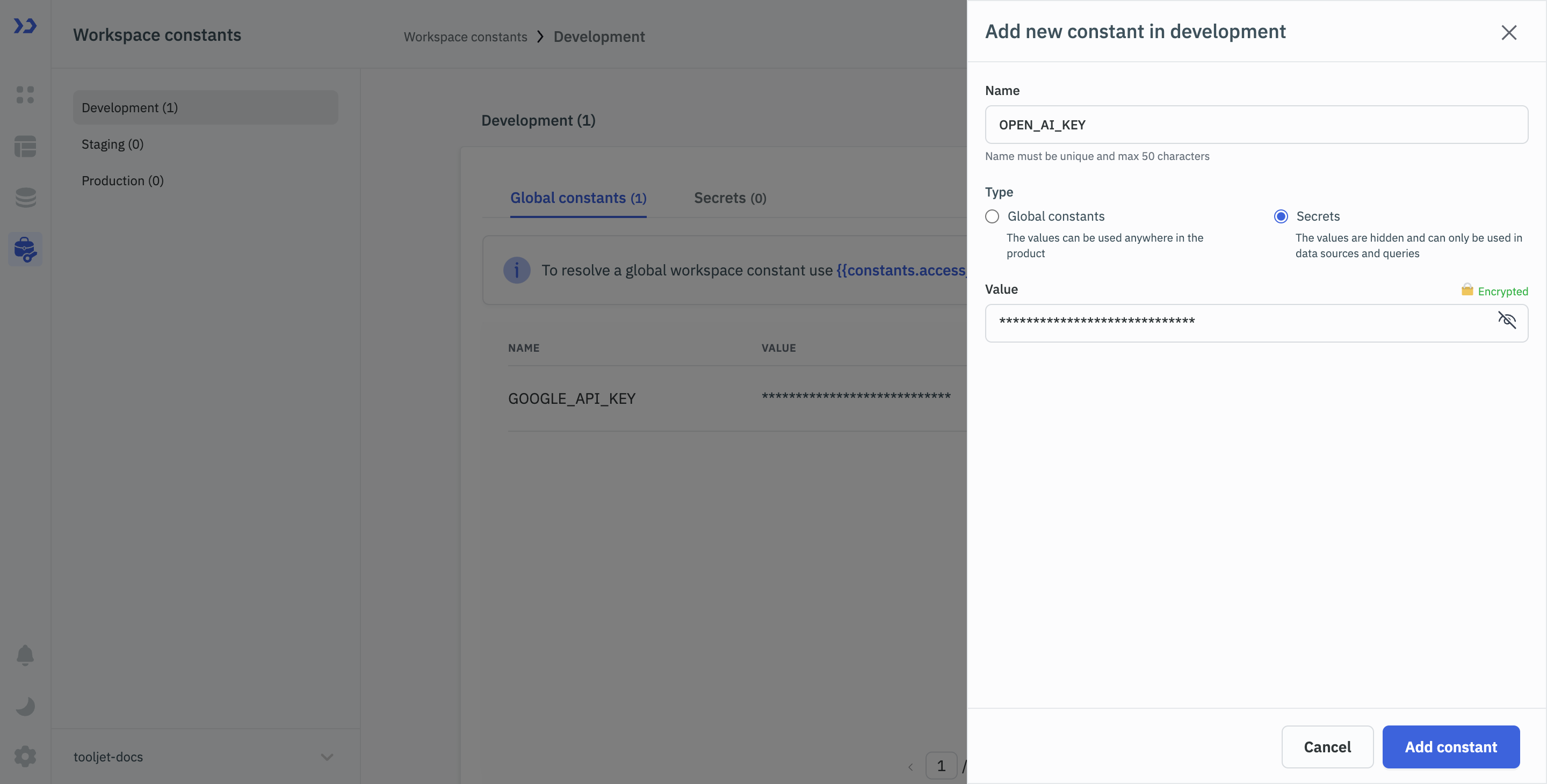
Click on Create new constant button to open the configuration drawer.
-
Enter a name and value for the workspace constant.
-
Select the type of workspace constant:
- Global constant
- Secret
-
Click the Add constant button to save.
Once a constant or secret is created, its type cannot be changed. You'll need to delete it and create a new one of the desired type.
Accessing Workspace Constants
Global Constants
Global constants can be accessed using the syntax {{constants.constant_name}} can be used in the app builder, data sources, data queries, and workflows.
In App Builder
Inside the App Builder, you can find all the constants inside the inspector element on the left sidebar.
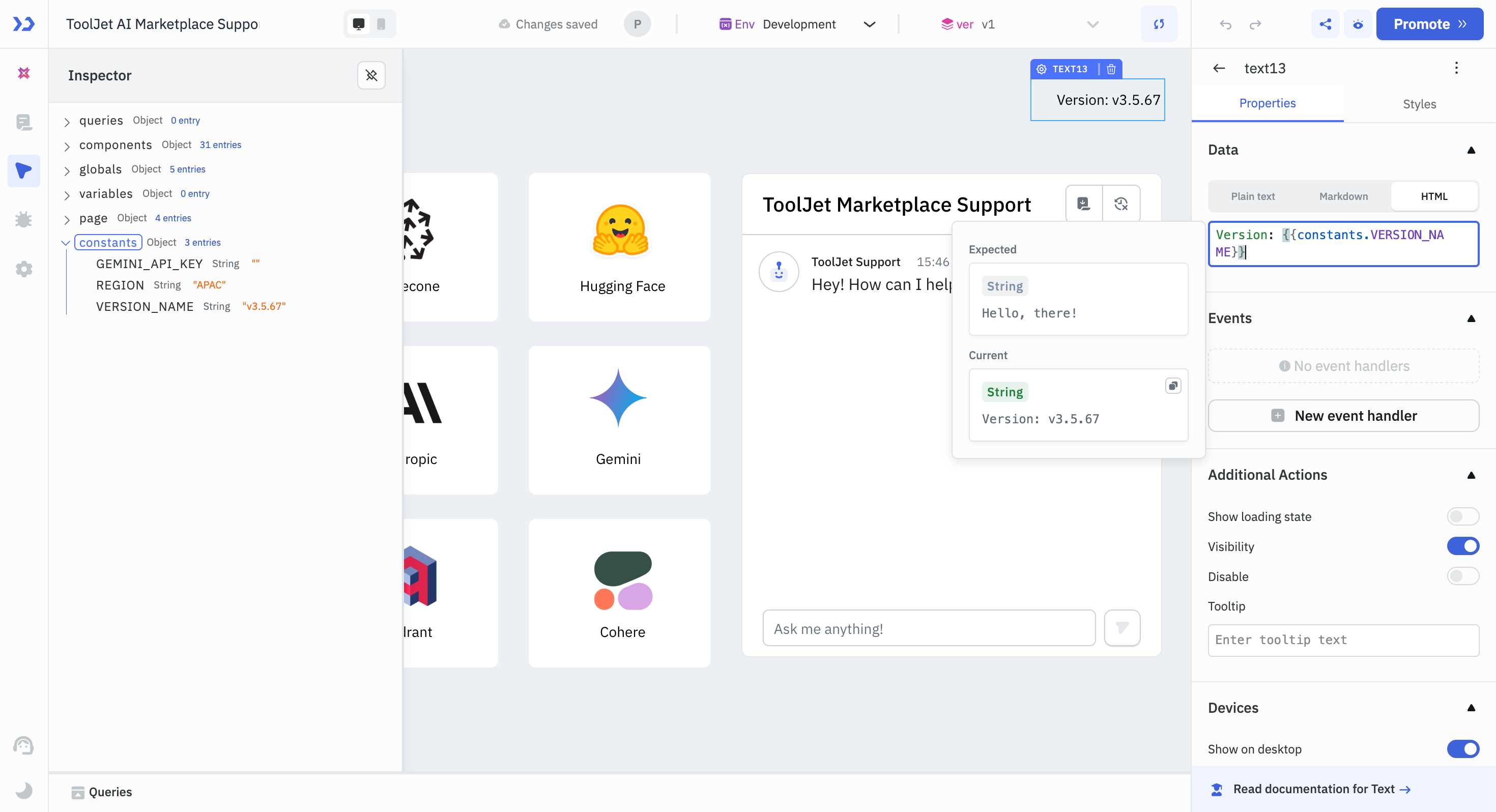
In Data Sources and Queries
Global constants in ToolJet allow you to define values once and reuse them across your data sources and queries.
-
Data Source Connection Form:
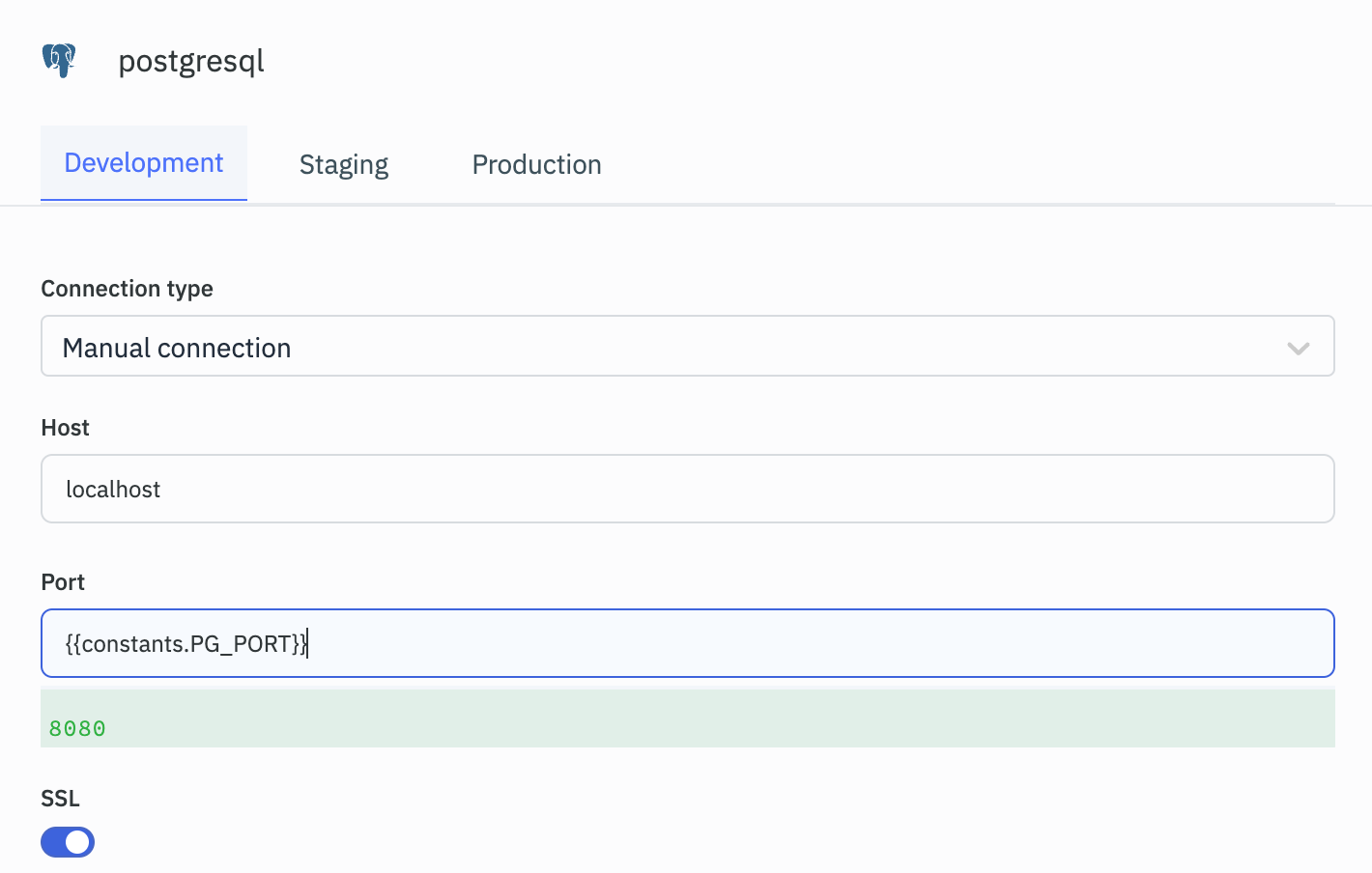
-
Inside Queries in Query Manager:
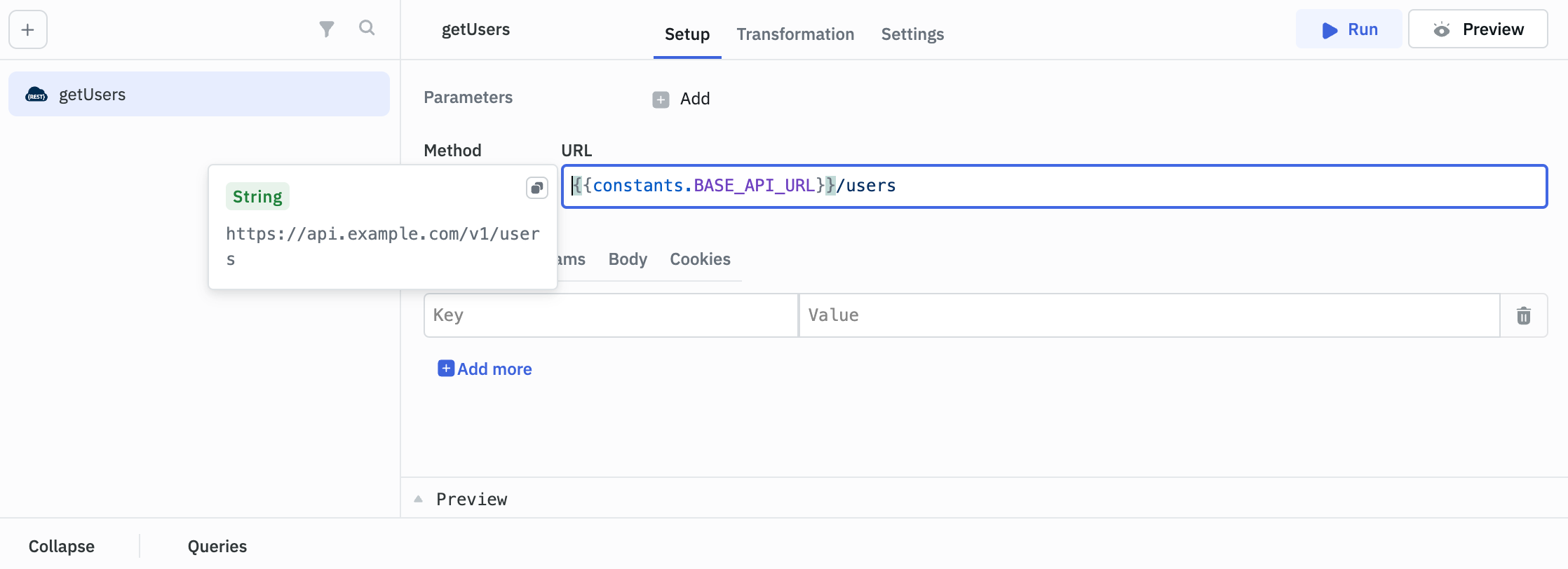
Using Secrets
Secrets are designed for secure storage of sensitive information like API keys, database credentials, and can be access using the syntax {{secrets.secret_name}}.
In Data Sources and Queries
In Data Sources and Queries, secret values are masked in the frontend and can only be viewed in the Workspace Constants dashboard.
-
Data Source Connection Form:
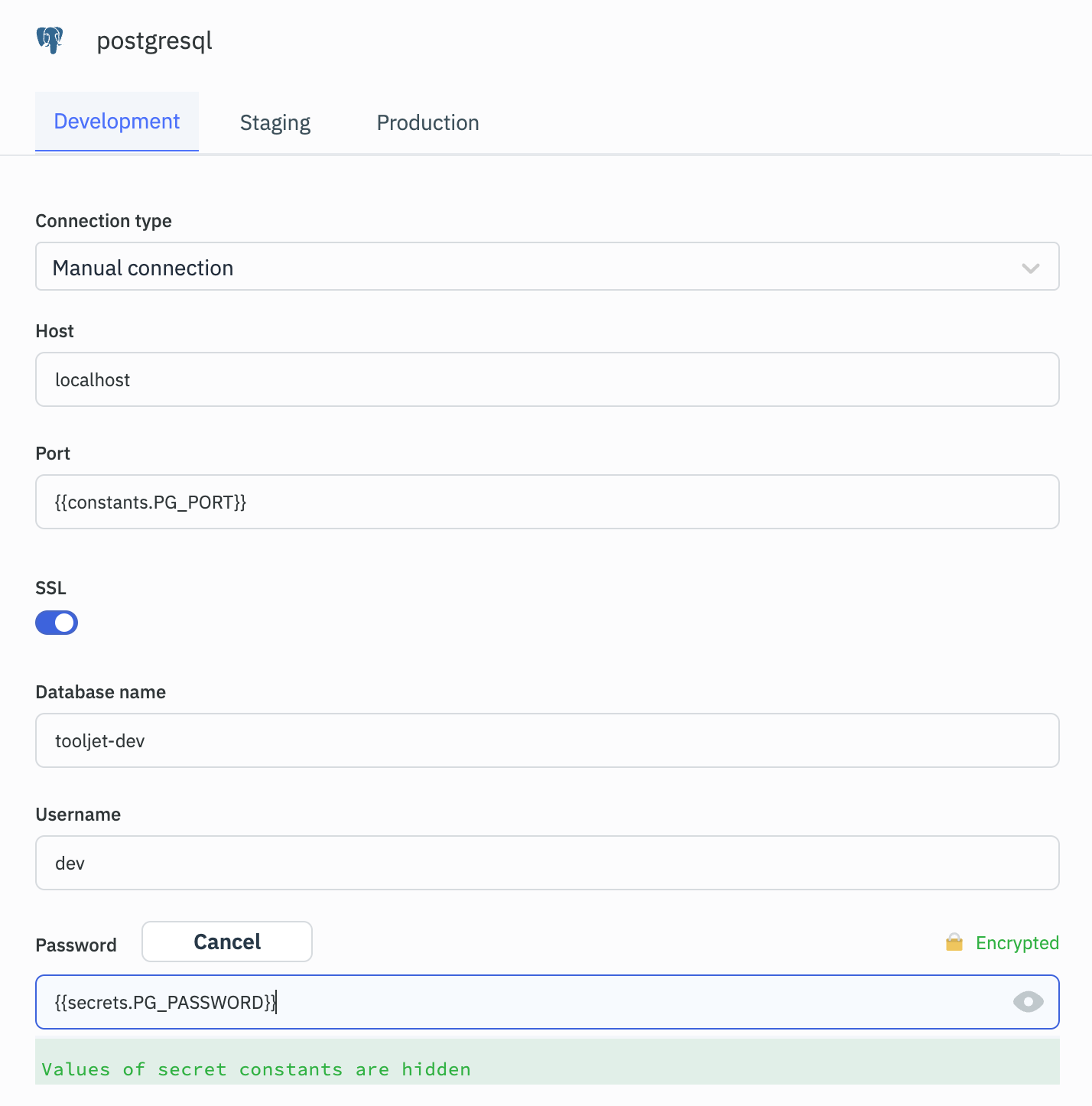
-
Inside Queries in Query Manager:
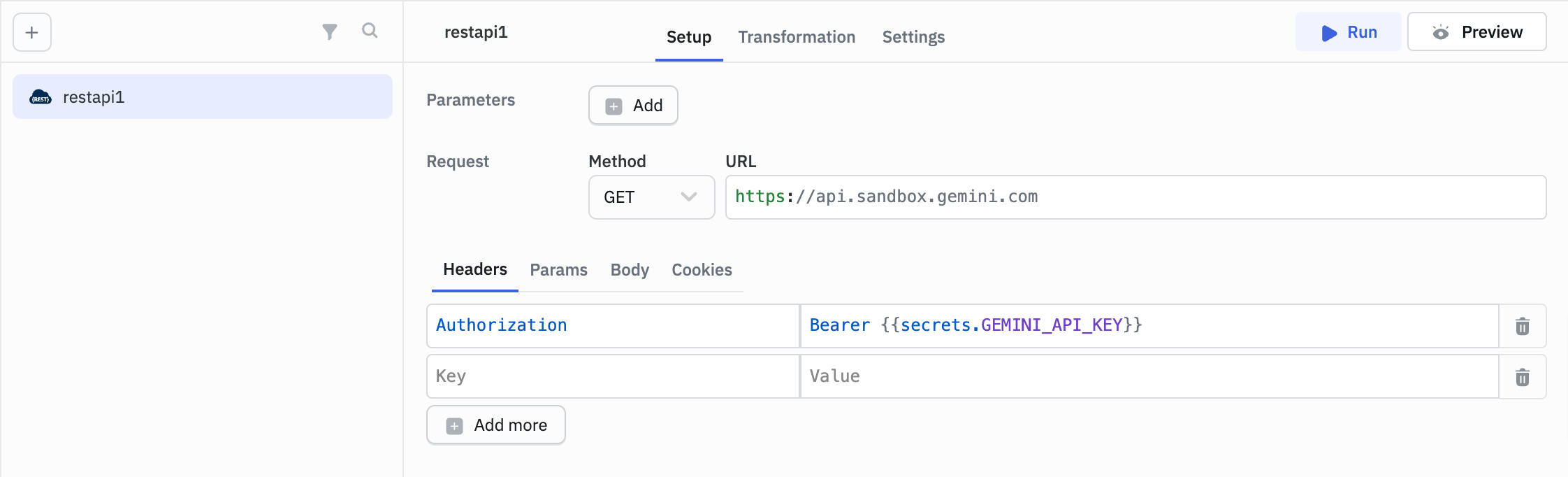
Mapping Workspace Constants from Environment Variables
From version v3.5.8-ee-lts, you can use environment variables to set global and secret constants. Workspace constants set using environment variables will have a .env tag in front of them. If there are two constants with the same name, the one set through the environment variable will be used in the app builder, while the constant set through the UI will have a duplicate tag in front of it.
Users cannot edit or delete constants created from environment variables through the UI. To add, update, or delete any values from an environment variable, the container must be restarted.
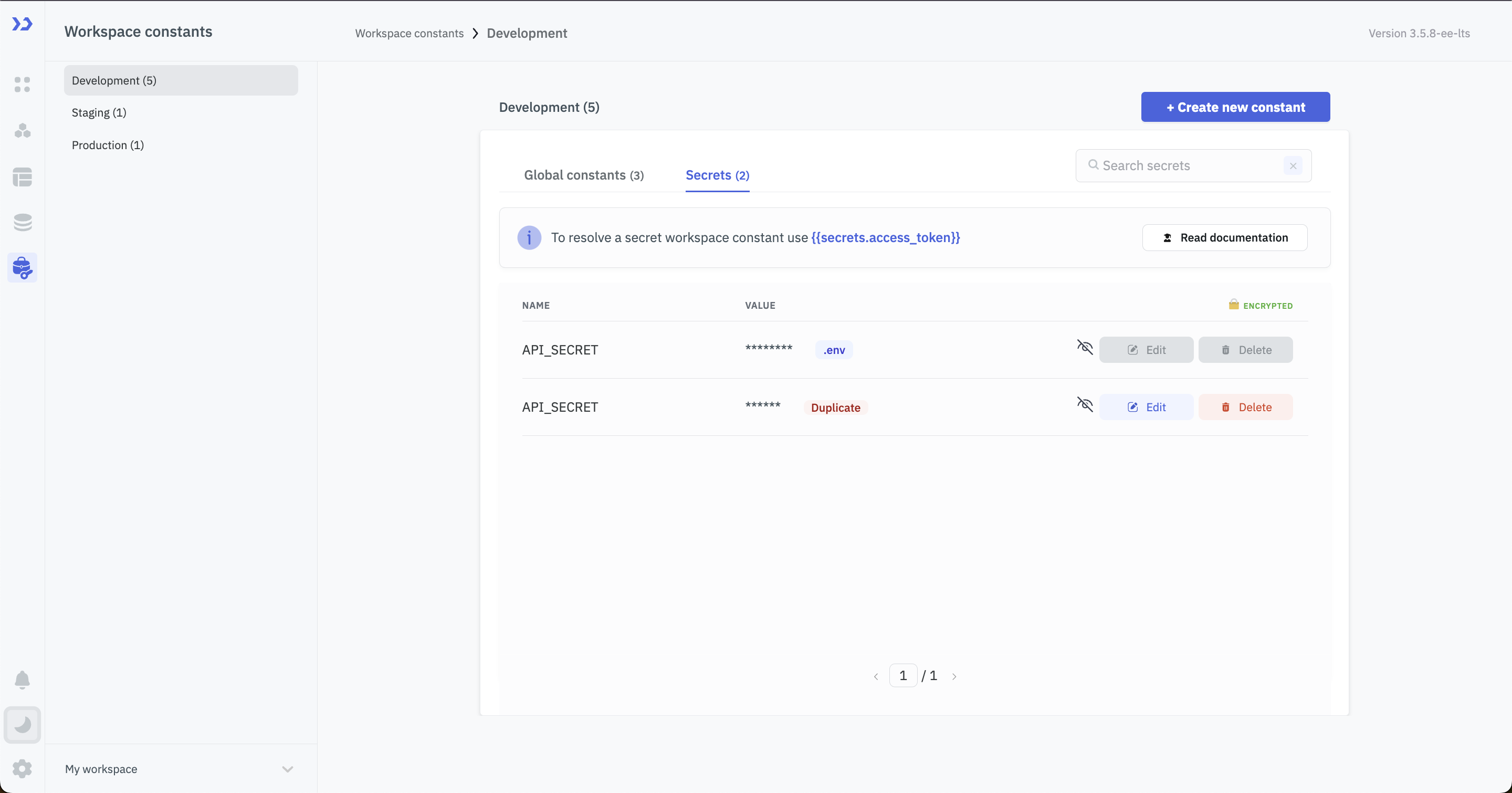
Setting Global Constants
Setting Individual Global Constant
Syntax - TOOLJET_GLOBAL_CONSTANTS__<environment>__constant_name
Example - TOOLJET_GLOBAL_CONSTANTS__development__companyName = "Corp Pvt. Ltd."
Setting Multiple Global Constants
Syntax - TOOLJET_GLOBAL_CONSTANTS__<environment> = {“name1”: “value1", “name2”: “value2"}
Example - TOOLJET_GLOBAL_CONSTANTS__development = {"company1": "corp.com", "company2": "example.com"}
Setting Secret Constants
Setting Individual Global Constant
Syntax - TOOLJET_SECRET_CONSTANTS__<environment>__constant_name
Example - TOOLJET_SECRET_CONSTANTS__development__apiKey = "agdagdagdg"
Setting Multiple Global Constants
Syntax - TOOLJET_SECRET_CONSTANTS__<environment> = {“name1”: “value1", “name2”: “value2"}
Example - TOOLJET_SECRET_CONSTANTS__development = {"api_url": "https://api.example.com", "password" : "12345", "key" : "agdagdagdg"}