Managing Variables
Variables in ToolJet allow you to store and manage temporary data across pages or within a single page. They’re useful for passing values between components, persisting state, and building dynamic applications.
This guide explains how to manage variables using code in your applications.
Set, Get, and Unset Variables
Setting, getting, and unsetting variables lets you control the state of a variable. Use set to create variables or update their values, get to access them in components or queries, and unset to delete them.
Set Variables
To set a variable in an application using code in a RunJS or RunPy query, use the setVariable function and pass the variable name and value.
actions.setVariable("<variableName>", "<variableValue>")
Example: If you’re building an internal tool for order management and want to store the orderId of a newly created order. You can use the following code:
actions.setVariable('currentOrderId', 'ORD-10293')
Similarly, if you want to set a page variable use the setPageVariable function:
actions.setPageVariable("<variableName>", "<variableValue>")
Example: If you want to set a page variable named userPreferences, with an object containing all the user preferences, like {theme:'dark', language:'en'}, you can use the following code:
actions.setPageVariable('userPreferences', { theme: 'dark', language: 'en' });
Get Variables
To access variables you can use the getVariable and getPageVariable functions. These functions take one argument: the name of the variable.
// To get app-level variable
actions.getVariable("<variableName>");
// To get page-level variable
actions.getPageVariable("<variableName>");
Example: If you previously stored a variable named currentOrderId and now want to access it, You can use the code below:
const orderId = actions.getVariable('currentOrderId');
Unset Variables
To unset(delete) a variable, you can use the unsetVariable and unsetPageVariable functions. These functions take one argument: the name of the variable.
// To delete app-level variable
actions.unsetVariable("<variableName>")
// To delete page-level variable
actions.unsetPageVariable("<variableName>")
Example: If you want to unset a page variable named userPreference, you would write:
actions.unsetPageVariable('userPreferences');
Use Cases
Sharing Data Across Pages
You can share data across different pages by setting a variable on one page and accessing it on another.
For instance, in a content management system, the homepage might display a list of posts (as shown in the image below). When a user clicks the View Post button, they’re taken to a new page to see the full content. To enable this, the postId is stored as a global variable so it can be accessed on both the homepage and the post details page.
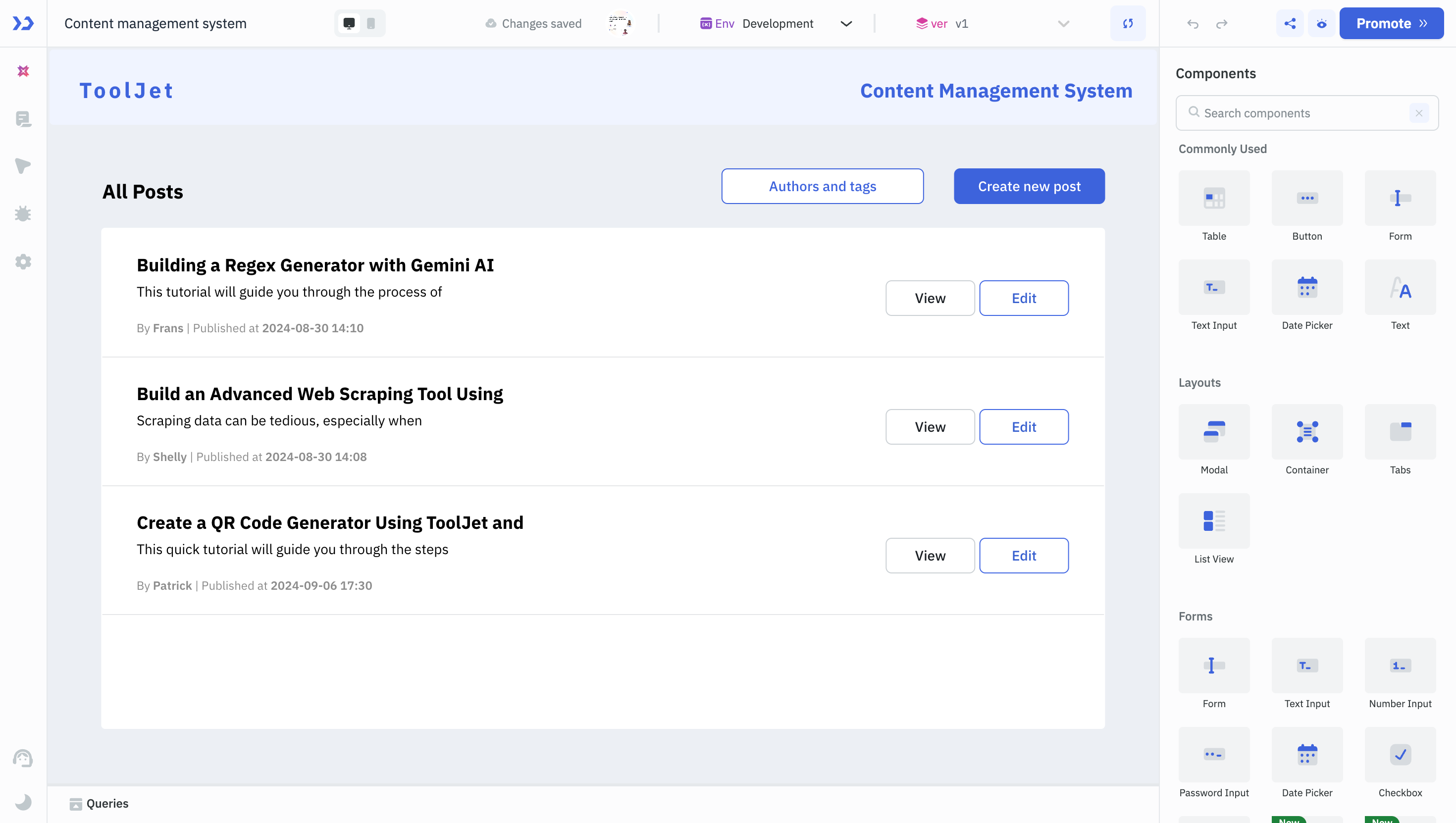
On the homepage, you could add a click event handler to the View Post button that sets a variable called selectedListViewIndex with the ID of the selected post. Then, on the second page, you could retrieve this variable and use it to fetch the full post from the database.
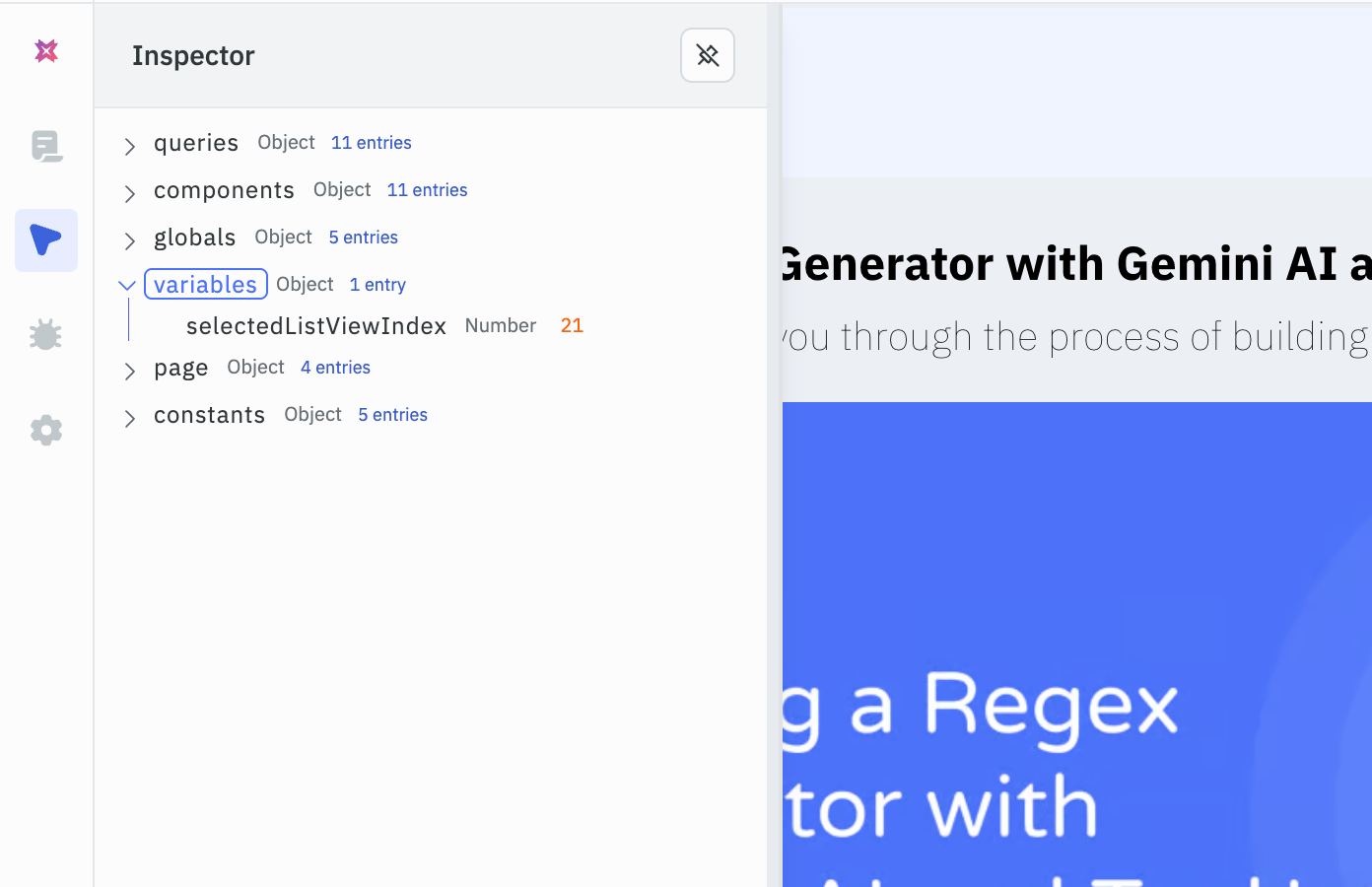
// Saving the post ID to a variable
actions.setVariable("selectedListViewIndex", components.postList.selectedRow.id);
// Retrieving the post ID
const postId = actions.getVariable("selectedListViewIndex");
Setting Up Form Payload for a Multi-Step Form
If you’re building a multi-step Form, each step may require different fields and appear on separate pages. You can use variables to construct the payload based on the currently active page.
Let’s say your Form has three steps: personal details, educational background, and work experience. Each step has its own set of fields. If you want to construct a final payload to be sent as the body when the submit button is clicked on the last step, you can create a RunJS query that checks which step is active and constructs the payload accordingly. Here’s how you might implement this:
let payload = {};
if (page.handle === "personalDetails") {
payload.firstName = components.firstName.value;
payload.lastName = components.lastName.value;
payload.email = components.email.value;
}
else if (page.handle === "education") {
payload.educationLevel = components.educationLevel.value;
payload.major = components.major.value;
payload.graduationYear = components.graduationYear.value;
}
else if (page.handle === "workExperience") {
payload.companyName = components.companyName.value;
payload.startDate = components.startDate.value;
payload.endDate = components.endDate.value;
payload.jobTitle = components.jobTitle.value;
}
actions.setVariable("formPayload", payload);
You can now pass this payload to a query that sends it to your backend API endpoint.
Variables help maintain data across pages, while page variables help manage localized, page-specific logic. Use page variables for temporary, page-specific UI state, and use app-level variables when data must persist across multiple pages.