Branching and Pull Requests
Branching and Pull Requests is currently in beta and not recommended for production use.
Branching enables multiple developers to work on an isolated copy of the application (their own branch) where changes don't affect others or the live production application until explicitly merged. Branching helps in protecting production quality through mandatory code reviews before changes go live and provide complete change history through Git integration, making every modification traceable and reversible.
When multiple developers need to build features or fix bugs in the same application, they need a way to work independently without disrupting each other or risking production stability. Branching solves this by:
- Protecting production quality through mandatory code reviews before changes go live
- Enabling parallel development, so teams can maintain speed without compromising on safety
- Providing complete change history through Git integration, making every modification traceable and reversible
When to Enable Branching?
Enable branching at the workspace level when:
- Multiple developers work on the same applications
- You need formal approval workflows before production changes
- Change tracking and review are organizational requirements
Understanding Branches and Versions
Master Branch and Sub-Branches
- Master Branch: The main branch containing your live application and its linear development history. The master branch is locked—changes can only enter through approved pull requests, never through direct edits.
- Sub-Branches: Independent copies created from the master branch where developers make changes freely. Each sub-branch is isolated until merged back to master.
Versions as Milestones
Versions exist only on the master branch, marking stable points in your application's development:
- Draft Version: The current working state on master (one active draft at a time).
- Saved Version: A finalized milestone, automatically committed to Git.
- Released Version: A version released from the production environment.
Sub-branches don't have versions, they themselves are working copies of a specific version.
Setting Up Branching
To enable branching you would need to configure the git sync. Follow the Git Sync Guide to configure it. Once Git Sync is configure then the branching is enabled by default (only for the beta version). Specify your Default Branch Name (typically "master" or "main"). This becomes your master branch where live applications reside.
ToolJet supports branching only over Git HTTPS. SSH is not supported.
Creating and Managing Branches
Create a New Branch
- Open your application
- Click the branch dropdown in the top navigation
- Select + Create New Branch
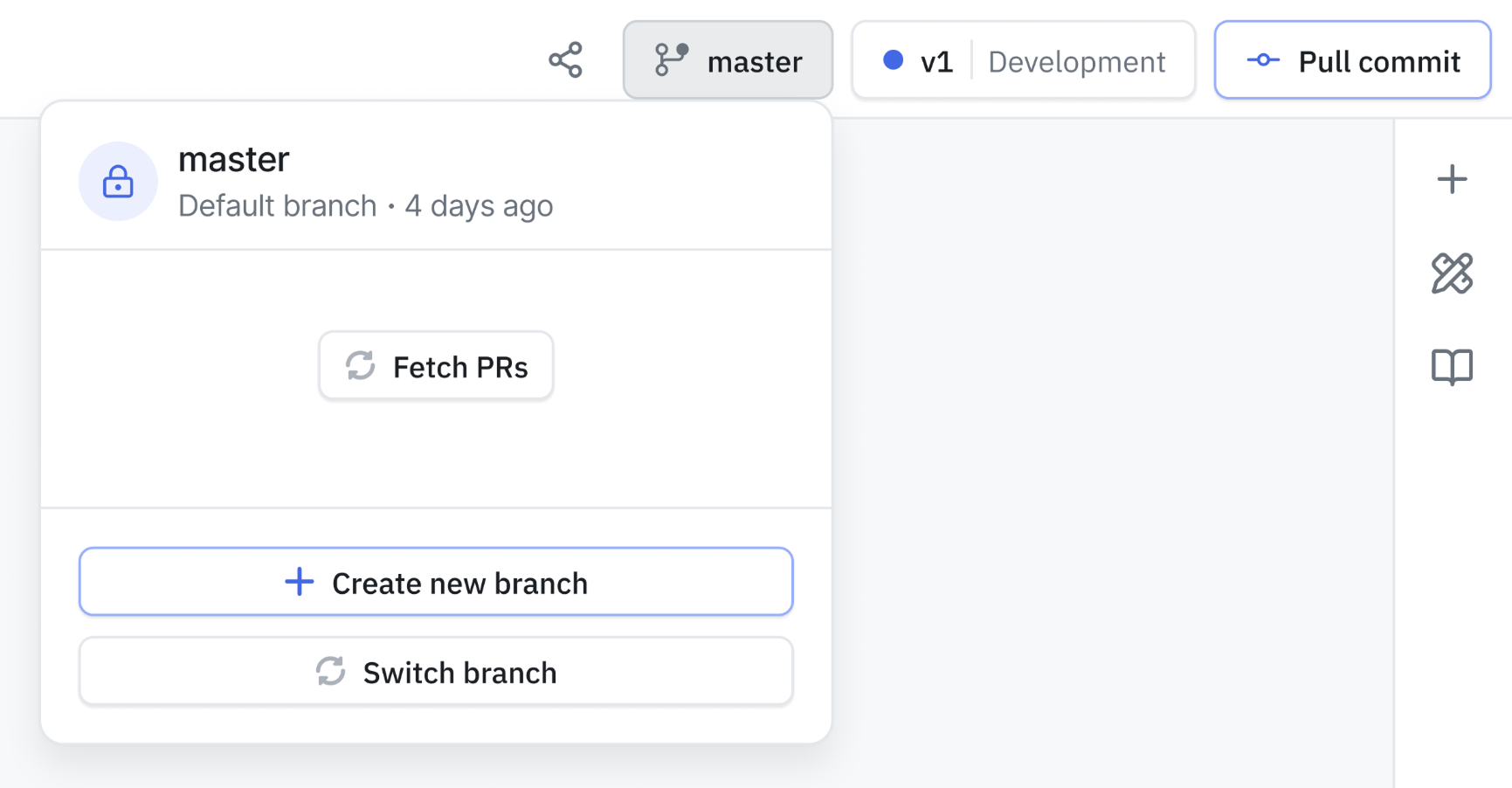
- Enter a descriptive branch name

- Choose the version to branch from (typically the current draft)
- Click Create Branch.
Your new branch is immediately available in ToolJet and automatically synced to Git.
Switch Between Branches
- Click the branch dropdown in the top navigation and then click on Switch Branch

- Select any active branch to switch
- All your edits now apply to the selected branch
Working with Pull Requests
Pull requests are how changes move from sub-branches to the master branch. All pull request management happens in your Git provider (GitHub, GitLab, etc.).
Push Changes to Git
Available only on sub-branches (master is locked):
- Make your changes in ToolJet
- Click Commit button in the top navigation
- Add a commit message describing your changes

- Click Commit Changes
Changes are committed to your current branch in Git.
Pull Changes from Git
On Master Branch:
- Ensure you're on the master branch with a draft version active
- Click Pull Commit
- Current draft is replaced with Git content
Create a Pull Request
A pull request is created in your Git provider, and the merge also happens there. All changes must be committed to Git to keep your application in sync.
- In ToolJet: Push your branch changes to Git
- Click Commit button in the top navigation
- Add a commit message describing your changes

- Click Commit Changes
- Create Pull Request
- After committing your changes, click the branch name in the navigation bar.
- Click the Create pull request button.
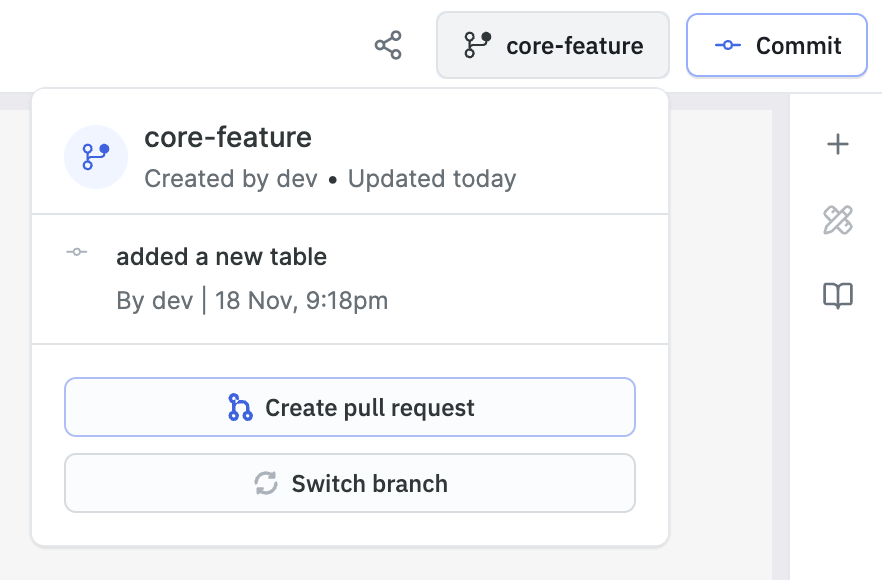
- You’ll be redirected to your Git provider to create the pull request. To keep the flow consistent, some fields are pre-filled. You can edit them or directly create the PR.
- Review and Approval:
- Add reviewers and description
- Submit for review
- Reviewers examine changes in Git
- Address any feedback or conflicts
- Approver merges the pull request
- In ToolJet: Pull merged changes into master
- Switch to the master branch and create a draft version
- Click Pull Commit
- Changes replace the current draft version
Creating Your First Released Version
Scenario: You've built a new application and need to release version 1.
- Create your application (master branch and draft v1 created automatically)
- Create a sub-branch from draft v1: developer/initial-build
- Develop your application on the branch
- Push changes to Git
- In Git: Create pull request, get approval, merge to master
- In ToolJet: Pull from Git into master branch
- Save draft v1 as version v1 (auto-commits to Git)
- Promote v1 to staging for testing
- Promote v1 to production
- Release v1
Parallel Development
Scenario: Two developers need to work on different features simultaneously.
- Developer A creates branch
johnson/inventoryfrom current master - Developer B creates branch
taylor/searchfrom current master - Both developers work independently and push their changes
- In Git:
- Both create pull requests to master
- Resolve any merge conflicts
- Manager approves both PRs
- Merge both branches to master
- In ToolJet:
- Create draft v2 from v1 (if no active draft exists)
- Pull changes from Git into draft v2
- Save v2 as a version
- Promote and release v2
Patching a Released Version
Scenario: Version 2 is released, version 3 is in draft, but v2 has a production bug requiring immediate fix.
Existing versions:
- v1 (Released)
- v2 (Released, needs patch)
- v3 (Draft, ongoing work)
Steps:
- Save draft v3 as v3 (preserves ongoing work)
- Create new draft v2.1 from v2
- Create branch
robert/patchfrom v2 - Make fixes on the patch branch and commit to Git
- In Git: Create PR, get approval, merge to master
- In ToolJet: Pull changes into draft v2.1
- Save v2.1 as a version
- Promote v2.1 to staging, then production
- Release v2.1
Creating and Saving Versions
Creating Draft Versions
On Master Branch Only:
- One active draft version at a time
- Create new draft from any saved version
- Draft represents the current working state
To create a new draft:
- Switch to master branch
- Click version dropdown → Create Draft
- Select the version to draft from
- Click Create
Saving Versions
When you save a draft version:
- Switch to master branch with active draft
- Click Save Version
- Enter version number (e.g., v2, v2.1)
- Click Save
- Version is automatically committed to Git
- Saved versions cannot be edited (locked state)
Important: Once saved, no further commits are allowed on that version. Saved versions represent completed milestones.
Branch Permissions
| Action | Master Branch | Sub-Branch |
|---|---|---|
| Direct edits | ❌ Only via PR | ✅ Yes |
| Push to Git | ❌ Not needed | ✅ Yes |
| Pull from Git | ✅ Draft only | ✅ Open branches |
| Rename | ❌ Git only | ❌ Git only |
| Close | ❌ Never | ❌ Git only |